Networking
Networkconcepts
1. Configuring interfaces and IPAddresses.
2. Configuring gateways and routes.
3. Basics of Name Resolution
4. DNS configuration on Linux systems
5. How to get started with core-dns
6. how docker uses network namespaces inernally
7. CLuster networking needs
8. Pod networking concepts
9. CNI --> Container Network Interface
10. ClusterDNS
11. Ingress networking
vagrantfile
# -*- mode: ruby -*-
# vi: set ft=ruby :
# All Vagrant configuration is done below. The "2" in Vagrant.configure
# configures the configuration version (we support older styles for
# backwards compatibility). Please don't change it unless you know what
# you're doing.
Vagrant.configure("2") do |config|
# The most common configuration options are documented and commented below.
# For a complete reference, please see the online documentation at
# https://docs.vagrantup.com.
# Every Vagrant development environment requires a box. You can search for
# boxes at https://vagrantcloud.com/search.
config.vm.box = "bento/ubuntu-18.04"
# Disable automatic box update checking. If you disable this, then
# boxes will only be checked for updates when the user runs
# `vagrant box outdated`. This is not recommended.
# config.vm.box_check_update = false
# Create a forwarded port mapping which allows access to a specific port
# within the machine from a port on the host machine. In the example below,
# accessing "localhost:8080" will access port 80 on the guest machine.
# NOTE: This will enable public access to the opened port
# config.vm.network "forwarded_port", guest: 80, host: 8080
# Create a forwarded port mapping which allows access to a specific port
# within the machine from a port on the host machine and only allow access
# via 127.0.0.1 to disable public access
# config.vm.network "forwarded_port", guest: 80, host: 8080, host_ip: "127.0.0.1"
# Create a private network, which allows host-only access to the machine
# using a specific IP.
# config.vm.network "private_network", ip: "192.168.33.10"
# Create a public network, which generally matched to bridged network.
# Bridged networks make the machine appear as another physical device on
# your network.
# config.vm.network "public_network"
# Share an additional folder to the guest VM. The first argument is
# the path on the host to the actual folder. The second argument is
# the path on the guest to mount the folder. And the optional third
# argument is a set of non-required options.
# config.vm.synced_folder "../data", "/vagrant_data"
# Provider-specific configuration so you can fine-tune various
# backing providers for Vagrant. These expose provider-specific options.
# Example for VirtualBox:
#
# config.vm.provider "virtualbox" do |vb|
# # Display the VirtualBox GUI when booting the machine
# vb.gui = true
#
# # Customize the amount of memory on the VM:
# vb.memory = "1024"
# end
#
# View the documentation for the provider you are using for more
# information on available options.
# Enable provisioning with a shell script. Additional provisioners such as
# Ansible, Chef, Docker, Puppet and Salt are also available. Please see the
# documentation for more information about their specific syntax and use.
# config.vm.provision "shell", inline: <<-SHELL
# apt-get update
# apt-get install -y apache2
# SHELL
end
Switches-Networks-Routers-Gateways -
network_basics
Switching, Routing, Gateways CNI in kubernetes.
Switching:
-------------------->
system-A(interface) switch(network-192.168.1.0) system-B(interface)
(192.168.1.10) (192.168.1.11)
systemA connects to systemB via switch(switch creates network) using interfaces("eth0").
to see list of interfaces in linux boxes use command "ip link":
------------------------------------------------------------------->
bharath@testvm:~$ sudo su
root@testvm:/home/bharath# ip link
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
2: ens4: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1460 qdisc mq state UP mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000
link/ether 42:01:0a:b4:10:03 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
root@testvm:/home/bharath#
Lets assume network IPAddress is "192.168.1.0"
We then assign the systems with IP address on the same network.
"On systemA:"
---------------------------------------------->
ip addr add 192.168.1.10/24 dev eth0
"on SystemB:"
------------------------------------------------>
ip addr add 192.168.1.11/24 dev eth0
once the links are UP and IP addresses are assigned, the computers can now communicate with eachother through the switch.
the switch can only enable communication within a network which means it can recieve packets
from a host on the network and deliver it to the other systems within the same network.
"from systemA(192.168.1.10)":
-------------------------------------------------->
ping 192.168.1.11
Reply from 192.168.1.11: bytes=32 time=4ms TTL=117
Reply from 192.168.1.11: bytes=32 time=4ms TTL=117
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------->
Now lets assume we have another network("192.168.2.0") and another two systems on the network("SystemC-192.168.2.10 and SystemD-192.168.2.11")
"Routing:"
=================================================================================================================>
How does a system in one network reach system in the other network.i.e.
How does the "sytemB(192.168.1.11)"in one netwrok reach "systemC(192.168.2.10" on the other network.
Thats where the "Router" comes in. "A Router helps connect two networks together"
"Router" is an intelligent device, so think of it as another server with many network ports.
Since it connects to the two separate networks it gets two IPs assigned. One on each network.
In the 1st network we assign "router an IP address 192.168.1.1" and
In the 2nd network we assign "router an IP aadress 192.168.2.1"
Now we have a router connected to the two networks that can enable communication between them.
Now, when systemB tries to send a packet to systemC, how does it know where the router is on the network to send the packet through?
the router is just another device on the network. There could be many other such devices.
Thats where we configure the systems with "a gateway" or "a route".
If the network is a room, the gateway is a door to the outside world or to the other networks or to the Internet.
The systems need to know where that door is to go through that.
to see the existing routing configuration on the system run the "route" command.
"route" command displays the kernel routing table and within that, as you can see there are no routing configurations as of now.
root@systemB:/home/bharath# route
Kernel IP routing table
Destination Gateway Genmask Flags Metric Ref Use Iface
root@systemB:/home/bharath#
so in this condtion our "SystemB" will not be able to reach "SystemC", it can only reach other systems in same network in the rane "192.168.1.0"
To configure gateway on "SystemB" to reach the networks on "192.168.2.0", run the "ip route add 192.168.2.0"
and specify that you can reach the "192.168.2.0" network through the door or gateway at "192.168.1.1"
the command is -> "ip route add 192.168.2.0/24 via 192.168.1.1"
Run the "route" command again
root@systemB:/home/bharath# route
Kernel IP routing table
Destination Gateway Genmask Flags Metric Ref Use Iface
192.168.2.0 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 UG 0 0 0 eth0
root@systemB:/home/bharath#
this route has to configure on all the systems i.e. if "SystemC" is to send back packet to "SystemB" then you need to add route on "SystemC's" routing table as well.
--> "ip route add 192.168.1.0/24 via 192.168.2.1"
root@systemC:/home/bharath# route
Kernel IP routing table
Destination Gateway Genmask Flags Metric Ref Use Iface
192.168.1.0 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0 UG 0 0 0 eth0
root@systemC:/home/bharath#
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------->
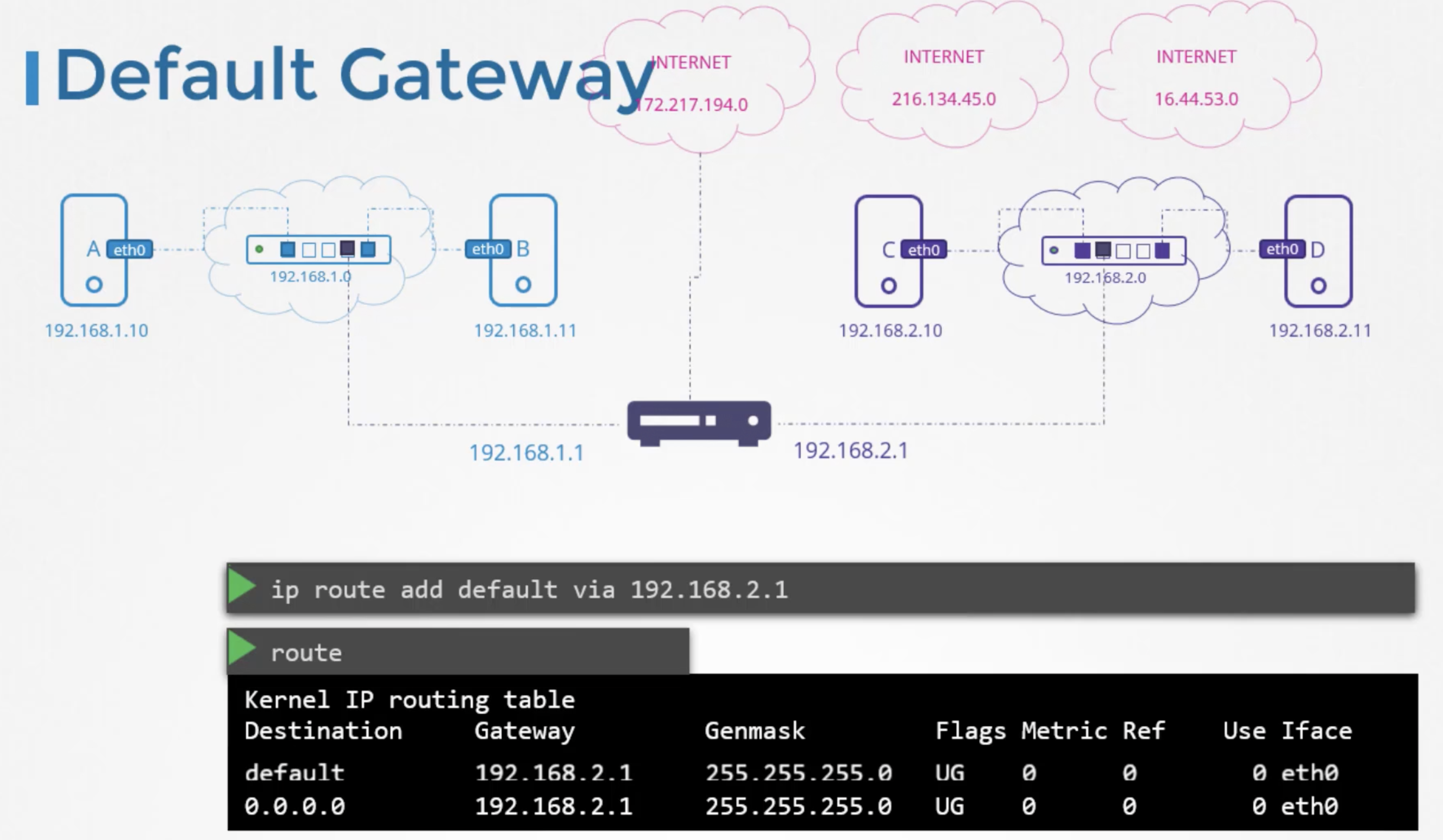
Now lets say these systems needs access to the internet. Say they need access to google at 172.217.194.0 network on the inernet.
so you connect the router to inernet and then add "ip route add 172.217.194.0/24" new route in your routing table to route all traffic to the network 172.217.194.0 through your router.
root@systemC:/home/bharath# route
Kernel IP routing table
Destination Gateway Genmask Flags Metric Ref Use Iface
192.168.1.0 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0 UG 0 0 0 eth0
172.217.194.0 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0 UG 0 0 0 eth0
root@systemC:/home/bharath#
there are so many different sites on different netwroks on the internet.
instead of adding a routing table entry for the same routers IP address for each of those networks.
you can simply say for any network that you dont know a route to, use this router as the default gateway.
This way any request to any network outside of your exisitng network goes to this particular router.
--> "ip route add default via 192.168.2.1"
root@systemC:/home/bharath# route
Kernel IP routing table
Destination Gateway Genmask Flags Metric Ref Use Iface
192.168.1.0 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0 UG 0 0 0 eth0
172.217.194.0 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0 UG 0 0 0 eth0
default 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0 UG 0 0 0 eth0
root@systemC:/home/bharath#
So in a simple setup like this, all you need is a single routing table entry with a default gateway set to the routers IP Address.
Instead of the word "default" we can also say "0.0.0.0/0" it means any IP destination, both are same actually
"ip route add 0.0.0.0/0 via 192.168.2.1"
root@systemC:/home/bharath# route
Kernel IP routing table
Destination Gateway Genmask Flags Metric Ref Use Iface
192.168.1.0 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0 UG 0 0 0 eth0
172.217.194.0 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0 UG 0 0 0 eth0
default 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0 UG 0 0 0 eth0
0.0.0.0/0 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0 UG 0 0 0 eth0
root@systemC:/home/bharath#
A 0.0.0.0/0 entry in the Gateway field indicates that you dont need a Gateway.
for example in this case for "SystemC" to access any devices in the 192.168.2.0 network it doesnt need a Gateway becuae it is in its own network.
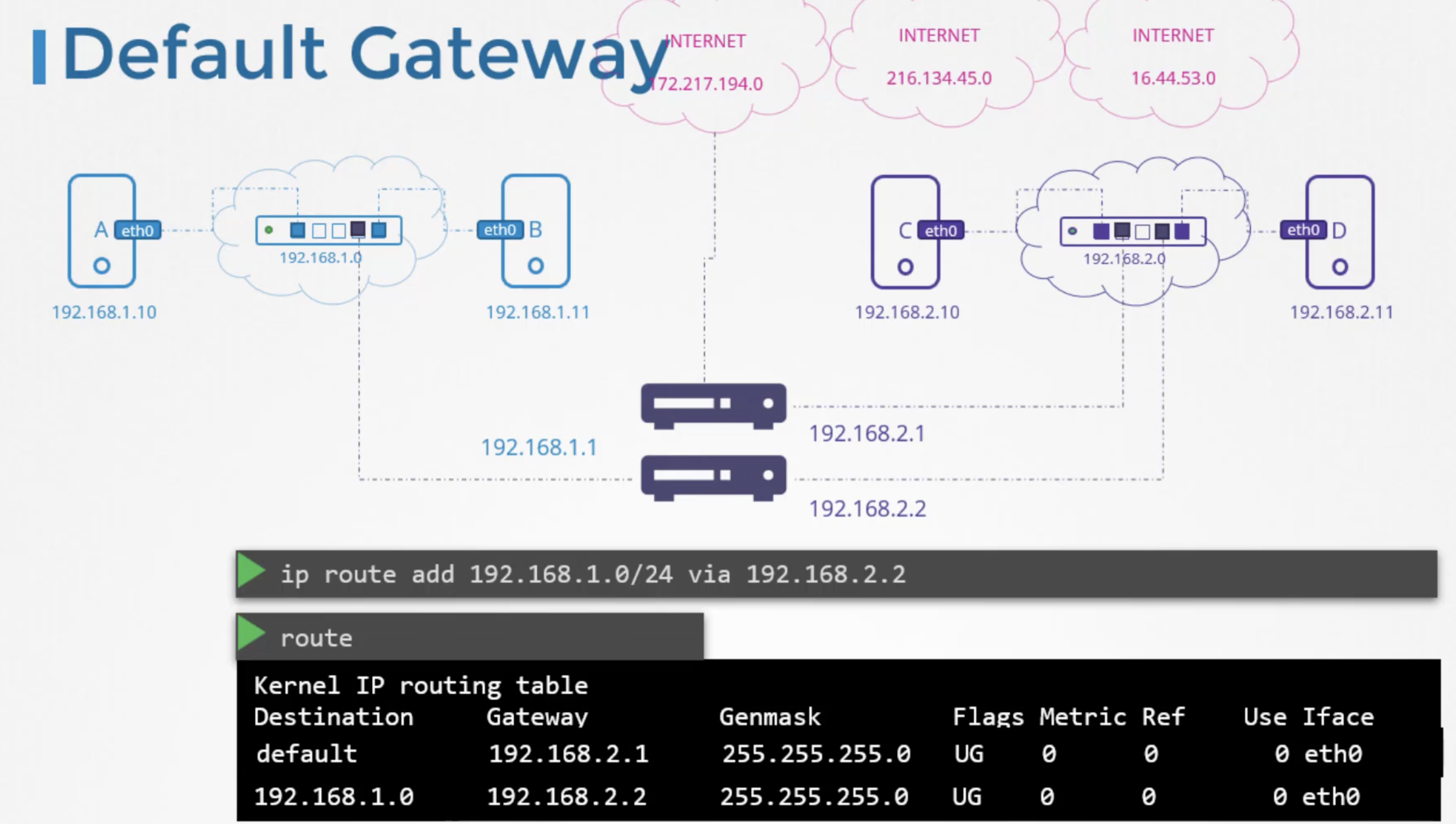
But say if we have multiple routers in our network one for the internet and another for the internal priavte network,
then we will need to have two separate route table entries for each network.
i.e. one entry for the internal priavte network and another entry with the default gateway for all other networks including public networks.
"ip route add 192.168.1.0/24 via 192.168.2.2"
"ip route add default via 192.168.2.1"
root@systemC:/home/bharath# route
Kernel IP routing table
Destination Gateway Genmask Flags Metric Ref Use Iface
192.168.1.0 192.168.2.2 255.255.255.0 UG 0 0 0 eth0
default 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0 UG 0 0 0 eth0
root@systemC:/home/bharath#
so if you are having issues reaching internet from your systems need to check this routing table and default gateway configuration.
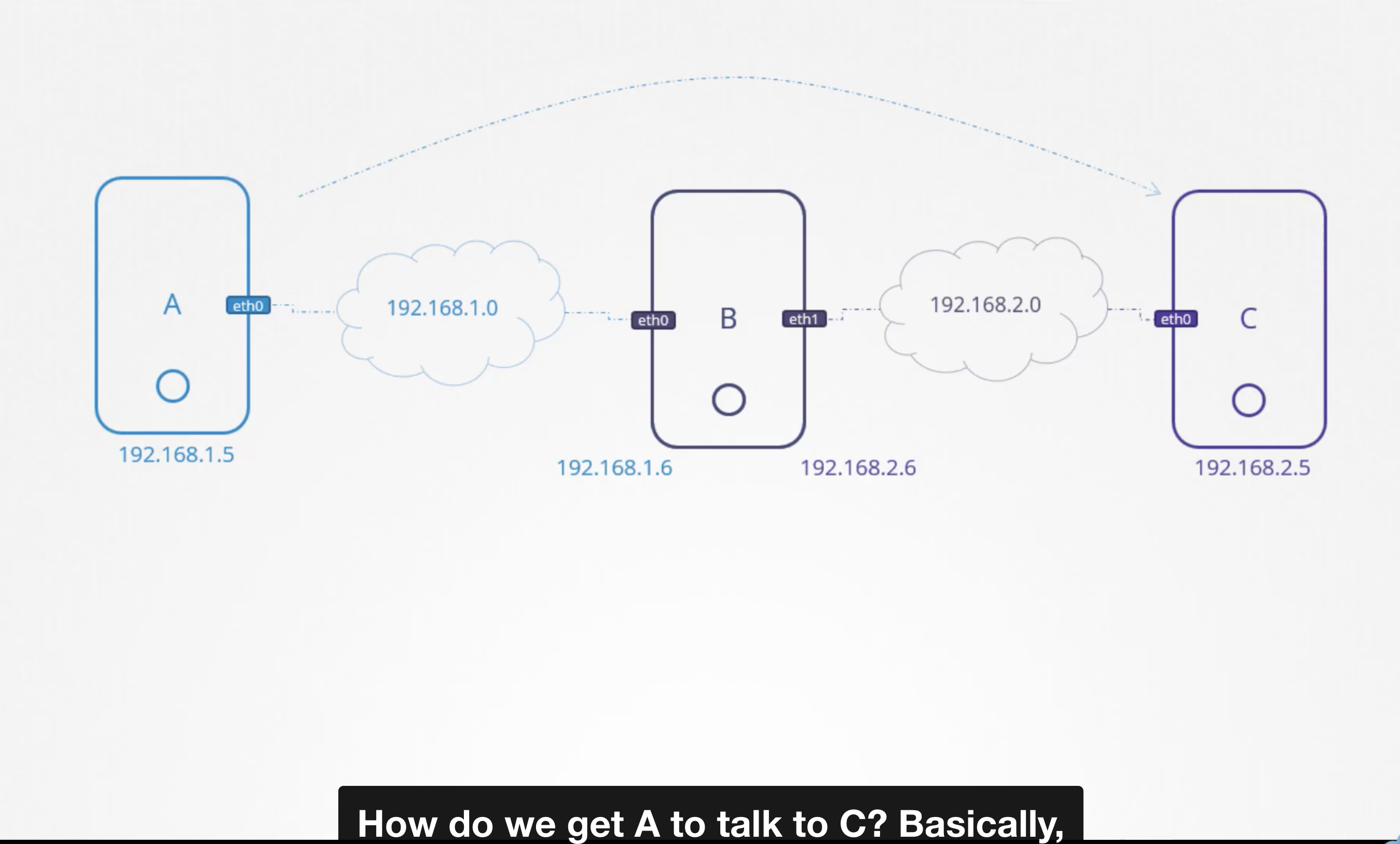
How to setup linux host a router:
------------------------------------------>
hostA (eth0)------192.168.1.0 -----(eth0) hostB (eth1) ------ 192.168.2.0 ---------(eth0) hostC
(192.168.1.5) (192.168.1.6) (192.168.2.6) (192.168.2.5)
ping from hostA to hostC:
-------------------------------->
ping 192.168.2.5
Connect: Network is unreachable
We need to tell hostA the door (or) gateway to network(192.168.2.0) is through host B, And we do that by adding routing table entry.
"ip route add 192.168.2.0/24 via 192.168.1.6"
if the packets were get through to hostC, hostC will have to send back responses to hostA.
when hostC tries to reach hostA at 192.168.1.0 netwotk, it would face the same issue.
so we need to let know the hostC to reach hostA through hostB ... here hostB acting as a router.
so we need to add an entry in hostCs routing table as below.
"ip route add 192.168.1.0/24 via 192.168.2.6"
Eventhough we added route table entry in both the hosts..still we are getting network unreachable error thats because
in Linux, packets are not forwarded from one interface to the next ...
i.e. for example packets recieved on eth0 on hostB are not forwarded to elsewhere through eth1, this is this way for security reasons.
for example if you had eth0 connected to your private network and eth1 to a public network,
We dont want anyone from the public network to easily send messages to the private network unless we explicitly allow that.
but in the above example we know that both are private networks and it is safe to enable communication between the two interfaces(eth0 and eth1).
we can allow hostB to forward packets from one network to thee other.
whether a host can forward packets between interfaces is governed by a setting in the system at file "/proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward"
cat /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward
0
by default the value in this file is set to 0 --> meaning no forward. set this to 1 and you should see the pings go through.
echo 1 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward
1
after reboot the setting may change..in order to make this change permanent update the same value in the "/etc/sysctl.conf" file
...
net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1
...
list of commands:
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------->
"ip link" --> list and modify the interfaces on the host.
"ip addr" --> this command is to see the ip addresses assigned to those interfaces.
"ip addr add 192.168.1.10/24 dev eth0" --> used to set IP addresses on the interfaces
changes with above commands only persists until you reboot the system ...if you want to make it permanent we need to set in the file "/etc/network/interfaces" file.
"ip route (or) route" --> used to view the routing table.
"ip route add 192.168.1.0/24 via 192.168.2.1" --> is used to add entry in the routing table.
"cat /etc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward"
dns_basics
Domain Name Resolution:
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------->
We have two hosts --> hostA and hostB ...both are part of same network.
hostA (eth0) --------------------------192.168.1.0------------------- (eth0) hostB
(192.168.1.10) (192.168.1.11)
ping 192.168.1.11
reply from 192.168.1.11: bytes=32 time=4ms TTL=117
reply from 192.168.1.11: bytes=32 time=4ms TTL=117
and we know that hostB has dabase services running on them. so instead of having to remember the IP Address of hostB, we decided to give it a name "DB"
Going forward we would like to ping hostB with the name "DB" instead of its IP Address.
to do that add an entry in "/etc/hosts" file of "hostA"
echo "192.168.1.11 db" >> /etc/hosts
so here, we told hostA that IP at 192.168.1.11 is a host named "db"
there is a catch here: hostA does not check to make sure if hostBs actual name is DB.
For example running a `hostname` command on hostB reveals that it is named "host-2" but hostA doesnot care.It goes by whats in the /etc/hosts file.
we can even put "192.168.1.11 www.google.com"
then "ping db" and "ping www.google.com" we will get response from hostB. We have two names pointing to the same system.
"ping db"
"ssh db"
"curl http://www.google.com"
above three domain-names points to hostB.
any ping/ssh/curl to the name, first it looks into the /etc/hosts file to findout the IP address of that host.
Translating hostname to IP Address this way is known as Name Resolution.
Within a small network of few systems, we can easily get away with the entries in the /etc/hosts file.
In each system we specify which are the other systems in the environment.
if systems(1000 or mnore) grows many, if any system changes its IP need to change all other systems "/etc/hosts" file.
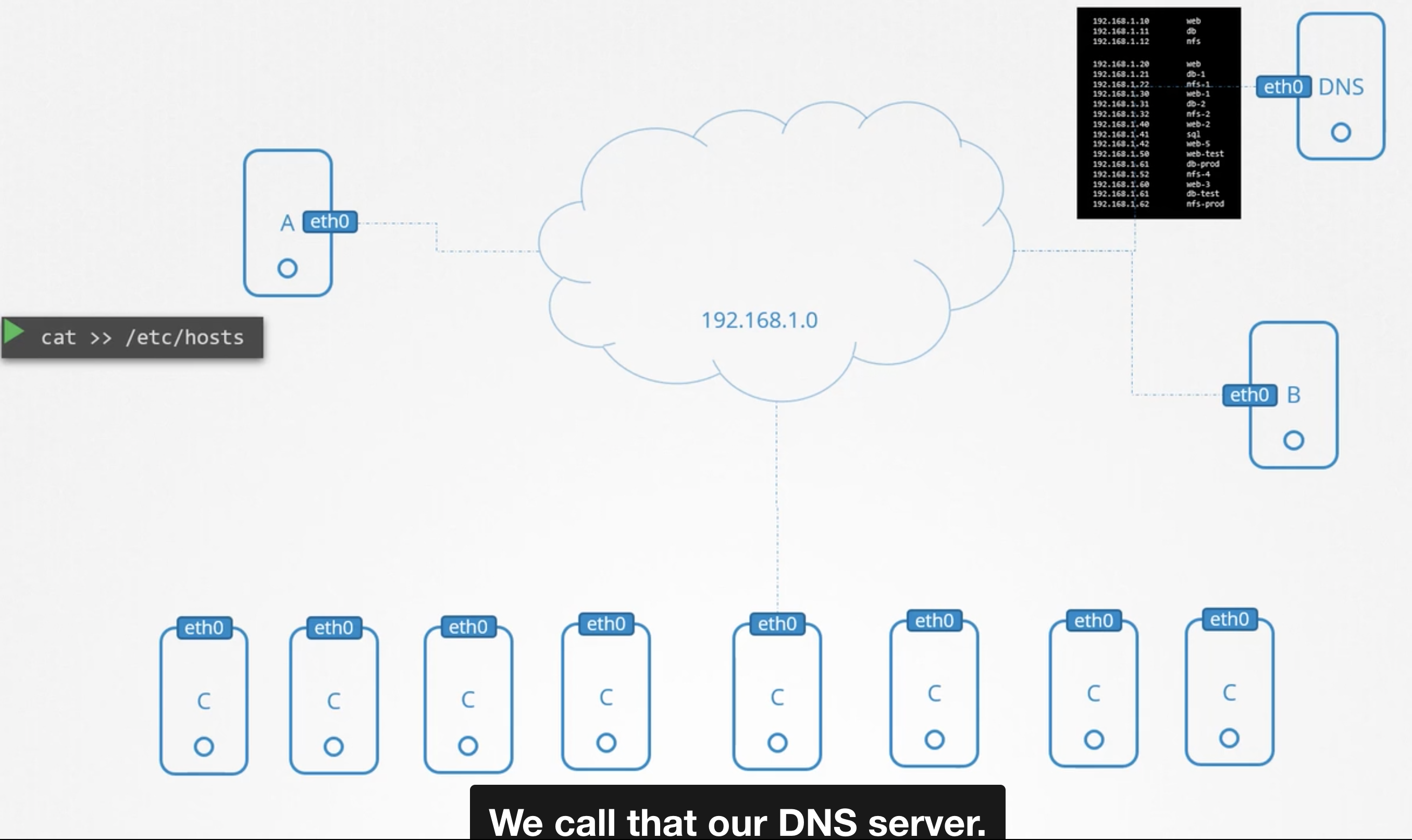
So to overcome this we move all those entries to one central server called DNS server.
And then we point all hosts to look up that server, if they need to resolve the hostname to an IP address instead of its own /etc/hosts files.
How do we point our host to DNS server:
------------------------------------------------------------------------>
DNS_Server_IP: 192.168.1.100
Every host has DNS resolution configuration file at /etc/resolv.conf, We can add an entry into it by adding the IPAddress of DNS server.
cat /etc/resolv.conf
nameserver 192.168.1.100
so if the same entry found at both "/etc/hosts" and DNSserver then priority goes to local lookup only i.e. "/etc/hosts".
but we can change this order of lookup by adding an entry in the file "/etc/nsswitch.conf" file.
cat /etc/nsswitch.conf
...
hosts: files dns
...
what if we "ping www.apple.com" it will fail cause we dont have any emntry for "www.apple.com" in both "/etc/hosts" file and in "DNS Server"
we can add another entry in "/etc/resolv.conf" file like below "nameserver 8.8.8.8" is a common well-known public name server available on the internet.
cat >> /etc/resolv.conf
nameserver 192.168.1.100
nameserver 8.8.8.8
for example if you want to map "web" to "web.mycompany.com" internally in your organization:
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------>
add an entry in "/etc/resolv.conf" as "search mycompany.com"
cat >> /etc/resolv.conf
nameserver 192.168.1.100
search mycompany.com
A --> IP to Domain name mapping
CNAME --> Name to Name mapping
"nslookup" does not consider the entries in the local "/etc/hosts" file. "nslookup" only queries the DNS server.
MacBook-Pro:certified_kubernetes_administrator bharathdasaraju$ nslookup www.google.com
Server: 8.8.8.8
Address: 8.8.8.8#53
Non-authoritative answer:
Name: www.google.com
Address: 74.125.24.106
Name: www.google.com
Address: 74.125.24.147
Name: www.google.com
Address: 74.125.24.103
Name: www.google.com
Address: 74.125.24.105
Name: www.google.com
Address: 74.125.24.104
Name: www.google.com
Address: 74.125.24.99
MacBook-Pro:certified_kubernetes_administrator bharathdasaraju$
MacBook-Pro:certified_kubernetes_administrator bharathdasaraju$ dig www.google.com
; <<>> DiG 9.10.6 <<>> www.google.com
;; global options: +cmd
;; Got answer:
;; ->>HEADER<<- opcode: QUERY, status: NOERROR, id: 60793
;; flags: qr rd ra; QUERY: 1, ANSWER: 6, AUTHORITY: 0, ADDITIONAL: 1
;; OPT PSEUDOSECTION:
; EDNS: version: 0, flags:; udp: 512
;; QUESTION SECTION:
;www.google.com. IN A
;; ANSWER SECTION:
www.google.com. 253 IN A 142.251.10.147
www.google.com. 253 IN A 142.251.10.105
www.google.com. 253 IN A 142.251.10.99
www.google.com. 253 IN A 142.251.10.103
www.google.com. 253 IN A 142.251.10.104
www.google.com. 253 IN A 142.251.10.106
;; Query time: 120 msec
;; SERVER: 8.8.8.8#53(8.8.8.8)
;; WHEN: Mon Sep 27 05:42:46 +08 2021
;; MSG SIZE rcvd: 139
MacBook-Pro:certified_kubernetes_administrator bharathdasaraju$
DNS in Linux -
Network Namespaces -
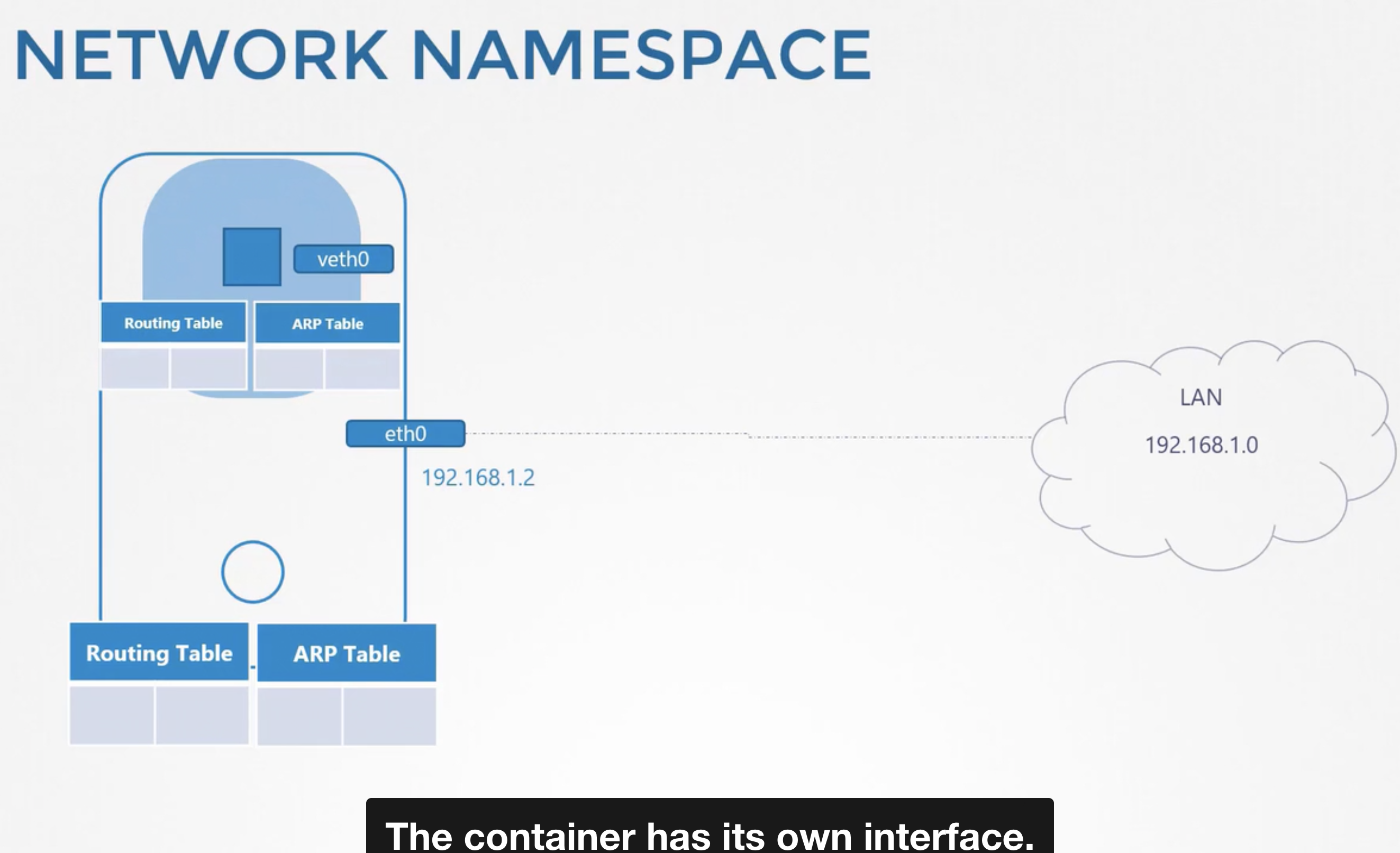

network_namespaces
Containers are separated from underlying host using namespaces
Our host has its own interfaces that connect to the local area network.
our host has its own routing and ARP tables with information about the rest of the network.
We want to see all of those details from the container.
when the container is created, we create network namespace for it, that way it has no visibility to any network-related information on the host.
within its namespace, the container can have its own virtual interfaces routing and ARP tables.
the container has its own interface.
Create network namespace:
--------------------------------------------------------------->
lets create two network namespaces("red" and "blue")
1. "ip netns add red"
2. "ip netns add blue"
list namespaces run "ip netns"
root@testvm:/home/bharath# ip netns add red
root@testvm:/home/bharath# ip netns add blue
root@testvm:/home/bharath# ip netns
blue
red
root@testvm:/home/bharath#
"To list interfaces in the host":
-------------------------------------->
root@testvm:/home/bharath# ip link
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
2: ens4: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1460 qdisc mq state UP mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000
link/ether 42:01:0a:b4:10:04 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
root@testvm:/home/bharath#
"how can we view the same interfaces(of course cant see hosts eth0) with in the network namespaces9(red, blue) created":
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------->
root@testvm:/home/bharath# ip netns exec red ip link
1: lo: <LOOPBACK> mtu 65536 qdisc noop state DOWN mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
root@testvm:/home/bharath# ip netns exec blue ip link
1: lo: <LOOPBACK> mtu 65536 qdisc noop state DOWN mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
root@testvm:/home/bharath#
root@testvm:/home/bharath# ip -n red link
1: lo: <LOOPBACK> mtu 65536 qdisc noop state DOWN mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
root@testvm:/home/bharath# ip -n blue link
1: lo: <LOOPBACK> mtu 65536 qdisc noop state DOWN mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
root@testvm:/home/bharath#
So with namespaces we have successfully prevented the container from seeing the hosts interface.
"The same is true with the ARP tables. i.e. can see ARP tables in host but not inside namespace i.e. inside container":
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------->
root@testvm:/home/bharath# arp
Address HWtype HWaddress Flags Mask Iface
10.180.16.1 ether 42:01:0a:b4:10:01 C ens4
root@testvm:/home/bharath#
root@testvm:/home/bharath# ip netns exec red arp
root@testvm:/home/bharath#
"The same is true with the routing tables . i.e. can see route tables in host but not inside namespace i.e. inside container":
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------->
root@testvm:/home/bharath# route
Kernel IP routing table
Destination Gateway Genmask Flags Metric Ref Use Iface
default 10.180.16.1 0.0.0.0 UG 0 0 0 ens4
10.180.16.1 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.255 UH 0 0 0 ens4
root@testvm:/home/bharath# ip netns exec red route
Kernel IP routing table
Destination Gateway Genmask Flags Metric Ref Use Iface
root@testvm:/home/bharath#
so as of now these namespaces have no network connectivity.
they have no interfaces of their own and they can not see the underlying host network.
"first establish the connectivity between the namespaces(red, blue) themselves:"
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------->
just like how we would connect two physical machines together using a cable to an ethernet interface on each machine.
we can connect two namespaces togethetr using a virtual ethernet pair (or) virtual cable. its often referred to as pipe.
its a virtual cable with two interfaces in either ends.
"to create a virtual cable(veth):"
------------------------------------>
root@testvm:/home/bharath# ip link add veth-red type veth peer name veth-blue
root@testvm:/home/bharath#
"the next step is to attach each interface to the appropriate namespace":
------------------------------------------------------------------------------->
root@testvm:/home/bharath# ip link set veth-red netns red
root@testvm:/home/bharath# ip link set veth-blue netns blue
root@testvm:/home/bharath#
root@testvm:/home/bharath# ip -n red link
1: lo: <LOOPBACK> mtu 65536 qdisc noop state DOWN mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
4: veth-red@if3: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST> mtu 1500 qdisc noop state DOWN mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000
link/ether 26:33:7c:ba:ed:3e brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff link-netns blue
root@testvm:/home/bharath# ip -n blue link
1: lo: <LOOPBACK> mtu 65536 qdisc noop state DOWN mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
3: veth-blue@if4: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST> mtu 1500 qdisc noop state DOWN mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000
link/ether a2:09:2b:8d:6b:b6 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff link-netns red
root@testvm:/home/bharath#
"We can then assign IP addresses to each of these namespaces":
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------->
we can use the usual "ip addr" command to assign the IPAddress but within each namespace.
root@testvm:/home/bharath# ip -n red addr add 10.180.16.5 dev veth-red
root@testvm:/home/bharath# ip -n blue addr add 10.180.16.6 dev veth-blue
root@testvm:/home/bharath#
"we then bring up the interface using the "ip link"":
---------------------------------------------------------------->
root@testvm:/home/bharath# ip -n red link set veth-red up
root@testvm:/home/bharath# ip -n blue link set veth-blue up
root@testvm:/home/bharath#
"now links are up...try a ping from the red namespace to reach the IP of the blue":
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------->
root@testvm:/home/bharath# ip netns exec red ping 10.180.16.6
PING 10.180.16.6 (10.180.16.6) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 10.180.16.6: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.023 ms
root@testvm:/home/bharath#
root@testvm:/home/bharath# ip netns exec red arp
Address HWtype HWaddress Flags Mask Iface
10.180.16.6 ether 21:01:0a:9b:10:1d C veth-red
root@testvm:/home/bharath#
root@testvm:/home/bharath# ip netns exec blue arp
Address HWtype HWaddress Flags Mask Iface
10.180.16.5 ether 09:18:d8:9b:6c:7b C veth-red
root@testvm:/home/bharath#
"but host doesnt know about these virtual namespace interfaces at all"
"how to connect multiple namespaces"
---------------------------------------->
Just like physical world you create a virtual network inside your host. to create network you need a switch.
so to create a virtual network you need a virtual switch.
you create a virtual switch witin per host and connect the namespaces with it.
"how to create a virtual switch within a host":
-------------------------------------------------->
there are multiple options
1. Linux Bridge
2. OpenvSwitch(OvS)
"Linux Bridge:"
--------------------->
to create internal bridge we add a new interface to the host using the "ip link add v-net-o type bridge"
root@testvm:/home/bharath# ip link add v-net-o type bridge
root@testvm:/home/bharath# ip link
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
2: ens4: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1460 qdisc mq state UP mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000
link/ether 42:01:0a:b4:10:04 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
5: v-net-o: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST> mtu 1500 qdisc noop state DOWN mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000
link/ether d6:f7:70:0b:c7:93 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
root@testvm:/home/bharath#
"bring v-net-0 interface up"
root@testvm:/home/bharath# ip link set dev v-net-o up
root@testvm:/home/bharath# ip linlk
Object "linlk" is unknown, try "ip help".
root@testvm:/home/bharath# ip link
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
2: ens4: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1460 qdisc mq state UP mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000
link/ether 42:01:0a:b4:10:04 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
5: v-net-o: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000
link/ether d6:f7:70:0b:c7:93 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
root@testvm:/home/bharath#
"v-net-0" --> network interface for the host, network switch for the namespaces.
"next step is to connect namespaces with this virtual network switch"
we need to connect all the namespace with the new bridge network, so we need new virtual cable for that purpose.
root@testvm:/home/bharath# ip -n red link del veth-red (when we delete this veth-blue automatically gets deleted also since they were pair.)
root@testvm:/home/bharath# ip -n blue link del veth-blue
Cannot find device "veth-blue"
root@testvm:/home/bharath#
"Create new virtual cable to connect to new bridge network"
root@testvm:/home/bharath# ip link add veth-red type veth peer name veth-red-br
root@testvm:/home/bharath# ip link add veth-blue type veth peer name veth-blue-br
root@testvm:/home/bharath#
"now the brides ready ... and connect them with namespaces"
root@testvm:/home/bharath# ip link set veth-red netns red
root@testvm:/home/bharath# ip link set veth-red-br master v-net-o
root@testvm:/home/bharath# ip link set veth-blue netns blue
root@testvm:/home/bharath# ip link set veth-blue-br master v-net-o
root@testvm:/home/bharath#
"set IP addresses for these links and turn them up"
root@testvm:/home/bharath# ip -n red addr add 10.180.16.10 dev veth-red
root@testvm:/home/bharath# ip -n blue addr add 10.180.16.11 dev veth-blue
root@testvm:/home/bharath# ip -n red link set veth-red up
root@testvm:/home/bharath# ip -n blue link set veth-blue up
root@testvm:/home/bharath#
root@testvm:/home/bharath# ip addr add 10.180.16.0/24 dev v-net-o
root@testvm:/home/bharath# ping 10.180.16.10
PING 10.180.16.10 (10.180.16.10) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 10.180.16.10: icmp_seq=1 ttl=4 time=0.023 ms
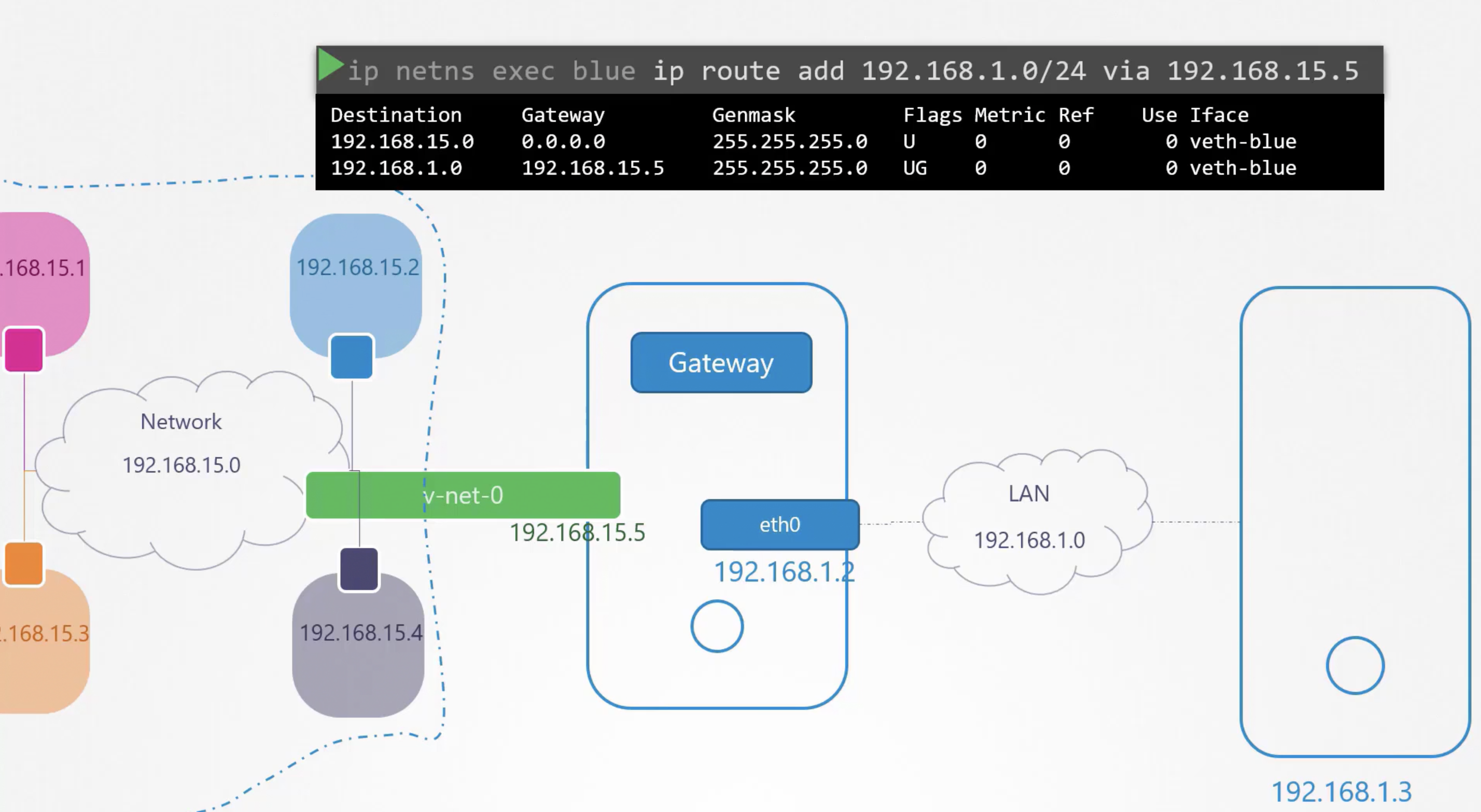
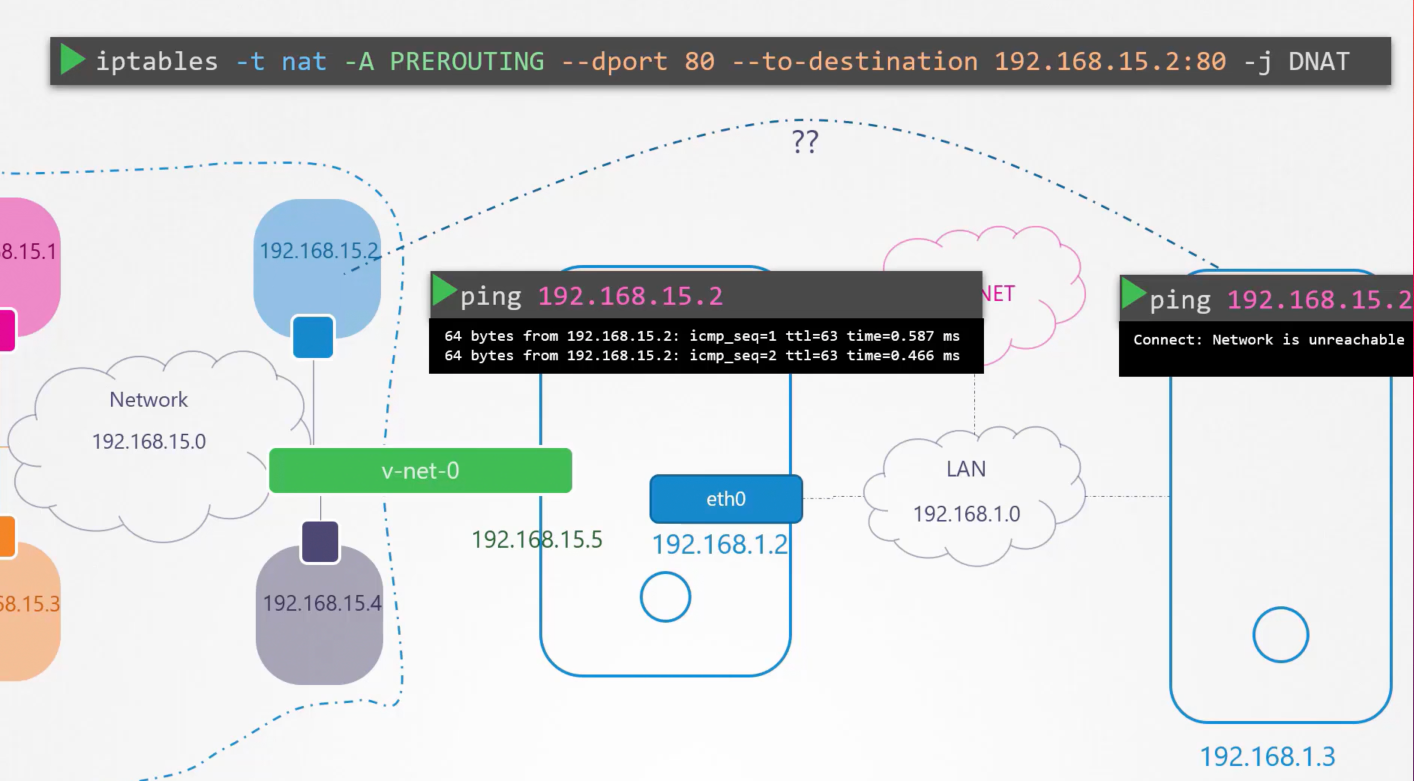
"We can even connect other LAN networks from namespace by adding gateway entry in the namespace routetable "
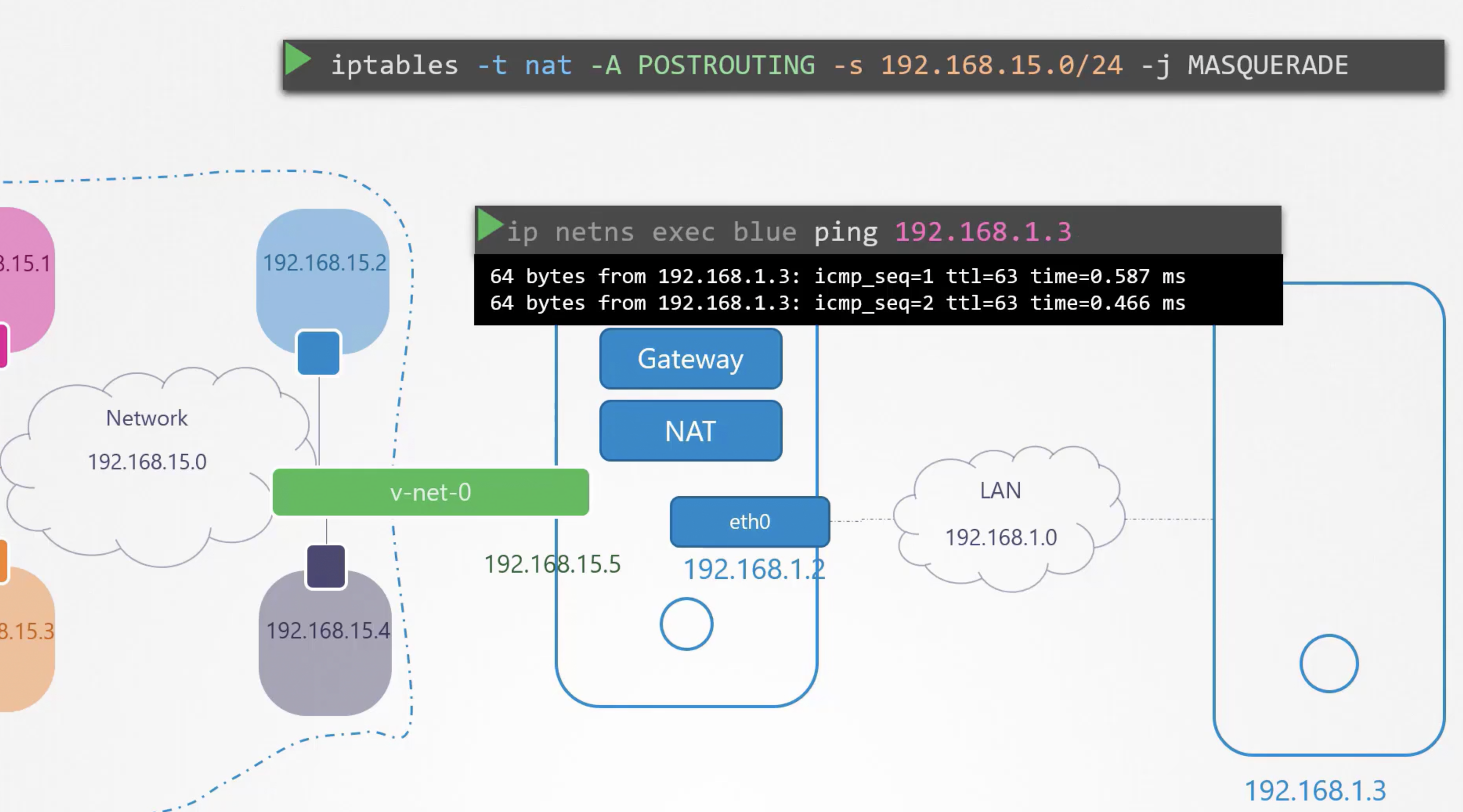
and also we need to add "Natting" rule in the host with below
"iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -s 10.180.16.0/24 -j MASQUERADE"
"how to reach the internet from namespace":
------------------------------------------------------------------------------->
root@testvm:/home/bharath# ip netns exec blue ping 8.8.8.8
connect: Network is unreachable
root@testvm:/home/bharath#
if outside network want to reach the namespace there are two options
1. Add gateway entry in route table to reach namespaces host
2. add an "iptables entry" i.e. "iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING --dport 80 --to-destination 10.180.16.11:80 -j DNAT"
docker_networking
"docker run --network none nginx"
"docker run --network host nginx"
"docker run --network bridge nginx"
bharath@bkubuntu:~$ docker network ls
NETWORK ID NAME DRIVER SCOPE
f2db6773d503 bridge bridge local
a1ce19f62cfa host host local
a1d8d71f1d61 none null local
bharath@bkubuntu:~$
bharath@bkubuntu:~$ ip link
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
2: ens4: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1460 qdisc fq_codel state UP mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000
link/ether 42:01:0a:b4:10:06 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
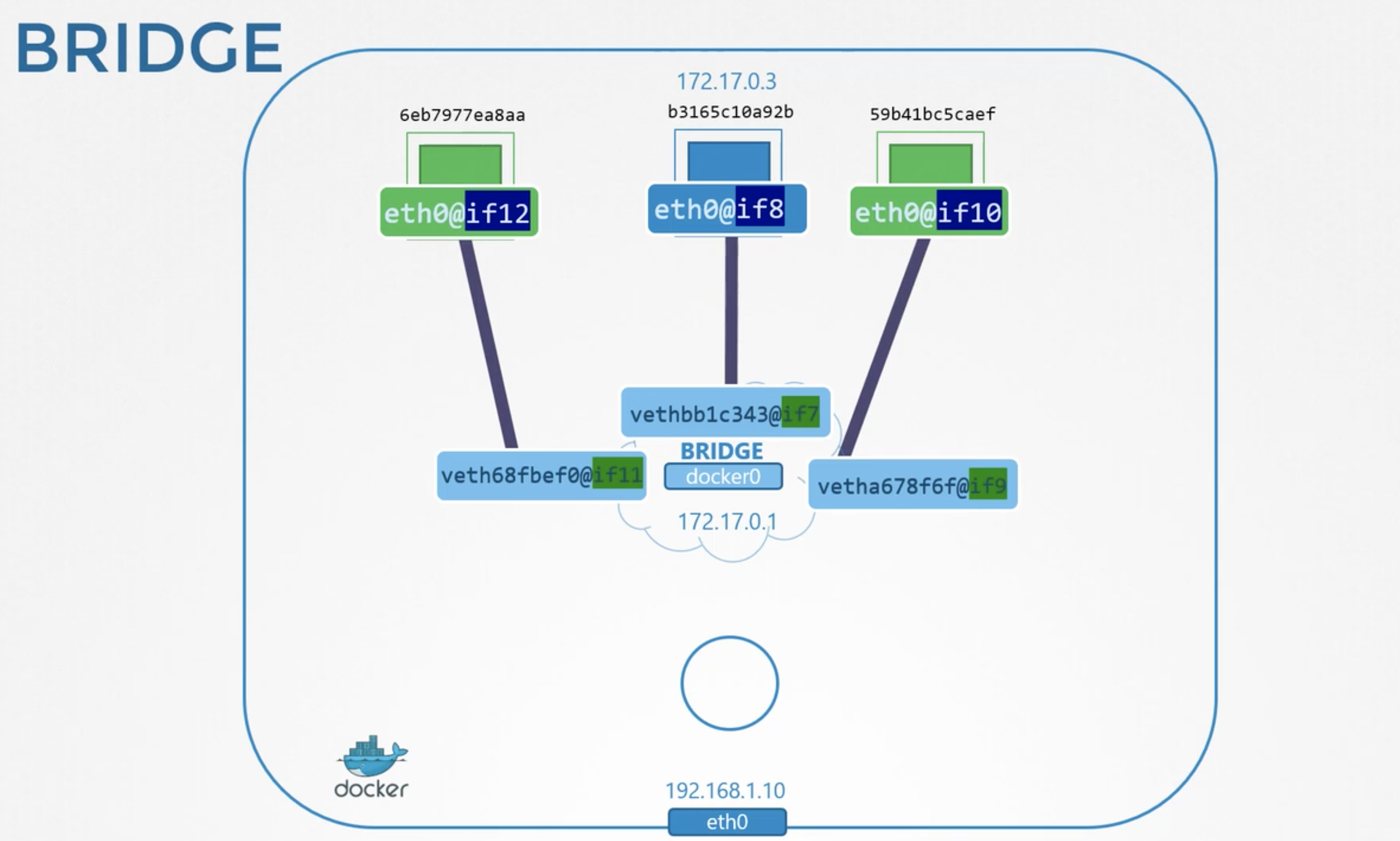
3: docker0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state UP mode DEFAULT group default
link/ether 02:42:48:99:09:93 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
5: veth3b4f54b@if4: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue master docker0 state UP mode DEFAULT group default
link/ether ee:bb:07:7c:1f:71 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff link-netnsid 0
bharath@bkubuntu:~$
bharath@bkubuntu:~$ ip addr
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 ::1/128 scope host
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
2: ens4: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1460 qdisc fq_codel state UP group default qlen 1000
link/ether 42:01:0a:b4:10:06 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 10.180.16.6/32 scope global dynamic ens4
valid_lft 3302sec preferred_lft 3302sec
inet6 fe80::4001:aff:feb4:1006/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
3: docker0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state UP group default
link/ether 02:42:48:99:09:93 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 172.17.0.1/16 brd 172.17.255.255 scope global docker0
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 fe80::42:48ff:fe99:993/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
5: veth3b4f54b@if4: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue master docker0 state UP group default
link/ether ee:bb:07:7c:1f:71 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff link-netnsid 0
inet6 fe80::ecbb:7ff:fe7c:1f71/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
bharath@bkubuntu:~$
root@bkubuntu:/home/bharath# ip netns list
1cf9ddf0126e (id: 0)
root@bkubuntu:/home/bharath#
root@bkubuntu:/home/bharath# ip netns list
1cf9ddf0126e (id: 0)
root@bkubuntu:/home/bharath#
root@bkubuntu:/home/bharath# docker inspect 0afdc5e4383f | grep -iA5 "Bridge"
"Bridge": "",
"SandboxID": "1cf9ddf0126e70b3bafcbd6348145a4094b4a342b82e9090a0bdd064222af4cb",
"HairpinMode": false,
"LinkLocalIPv6Address": "",
"LinkLocalIPv6PrefixLen": 0,
"Ports": {
--
"bridge": {
"IPAMConfig": null,
"Links": null,
"Aliases": null,
"NetworkID": "f2db6773d503c3eaa5aea03d99e6c3033b6aa768b3920303f31a80bc4fd8a3f7",
"EndpointID": "59e8399966f71306b79f3e1d5fbd3804378ff63008b3509a18c2e22998bd36ec",
root@bkubuntu:/home/bharath#
root@bkubuntu:/home/bharath# ip link
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
2: ens4: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1460 qdisc fq_codel state UP mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000
link/ether 42:01:0a:b4:10:06 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
3: docker0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state UP mode DEFAULT group default
link/ether 02:42:48:99:09:93 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
5: veth3b4f54b@if4: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue master docker0 state UP mode DEFAULT group default
link/ether ee:bb:07:7c:1f:71 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff link-netnsid 0
root@bkubuntu:/home/bharath#
root@bkubuntu:/home/bharath# ip netns list
1cf9ddf0126e (id: 0)
root@bkubuntu:/home/bharath#
root@bkubuntu:/home/bharath# ip -n 1cf9ddf0126e link
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
4: eth0@if5: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state UP mode DEFAULT group default
link/ether 02:42:ac:11:00:02 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff link-netnsid 0
root@bkubuntu:/home/bharath#
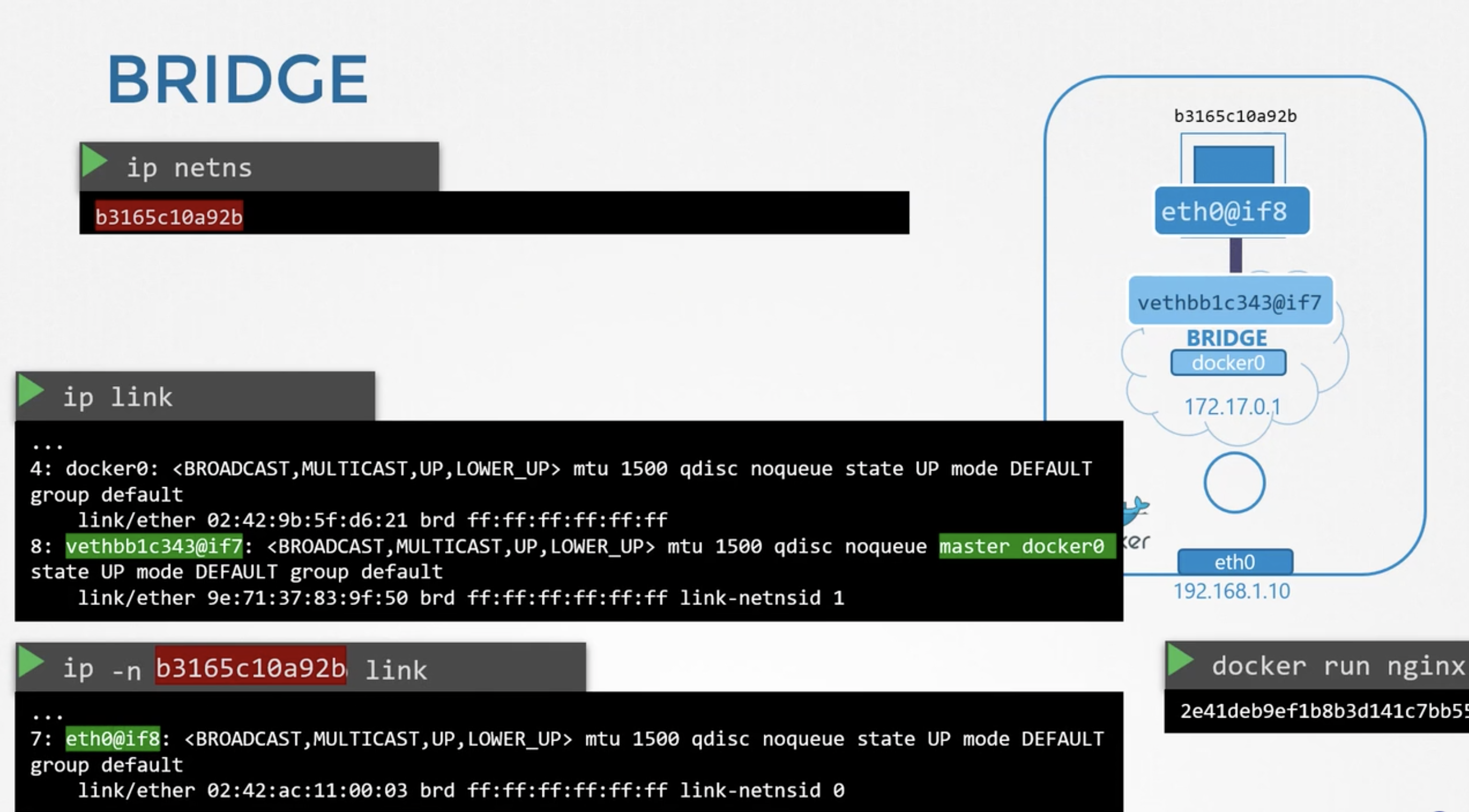
network namespace also gets an IPAddress.
root@bkubuntu:/home/bharath# ip -n 1cf9ddf0126e addr
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
4: eth0@if5: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state UP group default
link/ether 02:42:ac:11:00:02 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff link-netnsid 0
inet 172.17.0.2/16 brd 172.17.255.255 scope global eth0
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
root@bkubuntu:/home/bharath#
root@bkubuntu:/home/bharath# ip netns
1cf9ddf0126e (id: 0)
root@bkubuntu:/home/bharath# ip -n 1cf9ddf0126e addr
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
4: eth0@if5: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state UP group default
link/ether 02:42:ac:11:00:02 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff link-netnsid 0
inet 172.17.0.2/16 brd 172.17.255.255 scope global eth0
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
root@bkubuntu:/home/bharath# curl http://172.17.0.2:80
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Welcome to nginx!</title>
<style>
html { color-scheme: light dark; }
body { width: 35em; margin: 0 auto;
font-family: Tahoma, Verdana, Arial, sans-serif; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Welcome to nginx!</h1>
<p>If you see this page, the nginx web server is successfully installed and
working. Further configuration is required.</p>
<p>For online documentation and support please refer to
<a href="http://nginx.org/">nginx.org</a>.<br/>
Commercial support is available at
<a href="http://nginx.com/">nginx.com</a>.</p>
<p><em>Thank you for using nginx.</em></p>
</body>
</html>
root@bkubuntu:/home/bharath#
root@bkubuntu:/home/bharath# docker run -d -p 8080:80 nginx
bfc28c29eb3ebb88a56ea8f11cee0d44219cb3e0073922699828162f6702218b
root@bkubuntu:/home/bharath# docker ps
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
bfc28c29eb3e nginx "/docker-entrypoint.…" 3 seconds ago Up 2 seconds 0.0.0.0:8080->80/tcp, :::8080->80/tcp gracious_snyder
0afdc5e4383f nginx "/docker-entrypoint.…" 21 minutes ago Up 21 minutes 80/tcp agitated_mestorf
root@bkubuntu:/home/bharath#
MacBook-Pro:certified_kubernetes_administrator bharathdasaraju$ curl -k http://35.247.149.114:8080/
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Welcome to nginx!</title>
<style>
html { color-scheme: light dark; }
body { width: 35em; margin: 0 auto;
font-family: Tahoma, Verdana, Arial, sans-serif; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Welcome to nginx!</h1>
<p>If you see this page, the nginx web server is successfully installed and
working. Further configuration is required.</p>
<p>For online documentation and support please refer to
<a href="http://nginx.org/">nginx.org</a>.<br/>
Commercial support is available at
<a href="http://nginx.com/">nginx.com</a>.</p>
<p><em>Thank you for using nginx.</em></p>
</body>
</html>
MacBook-Pro:certified_kubernetes_administrator bharathdasaraju$
How does the docker forwards port from 8080 to 80.
Docker uses "iptables"
"iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -j DNAT --dport 8080 --to-destination 80"
"iptables -t nat -A DOCKER -j DNAT --dport 8080 --to-destination 172.17.0.2:80"
root@bkubuntu:/home/bharath# ip netns
802602f4ba1e (id: 1)
1cf9ddf0126e (id: 0)
root@bkubuntu:/home/bharath# docker ps
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
bfc28c29eb3e nginx "/docker-entrypoint.…" 22 minutes ago Up 22 minutes 0.0.0.0:8080->80/tcp, :::8080->80/tcp gracious_snyder
0afdc5e4383f nginx "/docker-entrypoint.…" 43 minutes ago Up 43 minutes 80/tcp agitated_mestorf
root@bkubuntu:/home/bharath#
root@bkubuntu:/home/bharath# iptables -nvL -t nat
Chain PREROUTING (policy ACCEPT 204 packets, 9466 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
371 18908 DOCKER all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 ADDRTYPE match dst-type LOCAL
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 204 packets, 9466 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 38 packets, 3115 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
0 0 DOCKER all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 !127.0.0.0/8 ADDRTYPE match dst-type LOCAL
Chain POSTROUTING (policy ACCEPT 40 packets, 3243 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
0 0 MASQUERADE all -- * !docker0 172.17.0.0/16 0.0.0.0/0
0 0 MASQUERADE tcp -- * * 172.17.0.3 172.17.0.3 tcp dpt:80
Chain DOCKER (2 references)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
0 0 RETURN all -- docker0 * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
2 128 DNAT tcp -- !docker0 * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 tcp dpt:8080 to:172.17.0.3:80
root@bkubuntu:/home/bharath#
container_network_interface
Container networking interface
CNI is a program with set of standards which creates all those network namespaces...VirtualEthernets
example: bridge add <cicd> <namespace>
CNI comes with set of supported plugins like:
1.Bridge
2.VLAN
3.IPVLAN
4.MACVLAN
5.WINDOWS
IPAM plugins:
--------------->
1.DHCP
2..host-local
some other plugins available from thirdparty organizations as well...
like Weave, flannel, cilium, calico, vmware nsx etc...
cluster_networking
Networking configuration on the master and worker nodes
Each node have atleast one interface must connected to a network.
Each interface must have an IPAddress connected.
The hosts must have unique hostname set, as well as unique MAC address
There are some ports should be opend as well. These are used by various components in the control plane.
The master should accept connections on "6443" port.
the worker nodes, kunectl tool, external users, and all other control plane components access kube-apiserver via this port.
the kubelets on the master and worker nodes listen on port "10250".
kube-scheduler port "10251" to be open.
kube-controller-manager requires port "10252" to be open.
The worker nodes exposes services(nodePort) for external access on ports "30000" to "32767" so these should be open as well.
ETCD server listens on port "2379"
if we have multiple masters all ports should open them as well and additional port "2380" should be opened so the etcd clients can communicate with each other.
network_concepts
ip link
ip addr
ip addr add 192.168.1.0/24 dev eth0
ip route
ip route add 192.168.1.0/24 via 192.168.2.1
cat /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward
arp
route
how to deploy a network addon --> "weave-net"
root@controlplane:~# kubectl get nodes -o wide
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION INTERNAL-IP EXTERNAL-IP OS-IMAGE KERNEL-VERSION CONTAINER-RUNTIME
controlplane Ready control-plane,master 7m7s v1.20.0 10.3.110.9 <none> Ubuntu 18.04.5 LTS 5.4.0-1052-gcp docker://19.3.0
node01 Ready <none> 6m11s v1.20.0 10.3.110.12 <none> Ubuntu 18.04.5 LTS 5.4.0-1052-gcp docker://19.3.0
root@controlplane:~#
root@controlplane:~# ip link
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
2: docker0: <NO-CARRIER,BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state DOWN mode DEFAULT group default
link/ether 02:42:1b:24:29:2c brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
3: flannel.1: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1400 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN mode DEFAULT group default
link/ether ce:f4:d8:2e:e4:ae brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
4: cni0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1400 qdisc noqueue state UP mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000
link/ether ae:27:5f:22:d2:18 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
5: veth9b446119@if3: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1400 qdisc noqueue master cni0 state UP mode DEFAULT group default
link/ether 1e:50:5b:2f:68:df brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff link-netnsid 2
6: veth96d95d6c@if3: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1400 qdisc noqueue master cni0 state UP mode DEFAULT group default
link/ether 92:68:a5:7e:f2:3d brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff link-netnsid 3
44603: eth0@if44604: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1450 qdisc noqueue state UP mode DEFAULT group default
link/ether 02:42:0a:03:6e:09 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff link-netnsid 0
44605: eth1@if44606: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state UP mode DEFAULT group default
link/ether 02:42:ac:19:00:1c brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff link-netnsid 1
root@controlplane:~#
What is the network interface configured for cluster connectivity on the master node?
node-to-node communication
root@controlplane:~# ip addr
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
2: docker0: <NO-CARRIER,BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state DOWN group default
link/ether 02:42:1b:24:29:2c brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 172.12.0.1/24 brd 172.12.0.255 scope global docker0
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
3: flannel.1: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1400 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default
link/ether ce:f4:d8:2e:e4:ae brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 10.244.0.0/32 brd 10.244.0.0 scope global flannel.1
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
4: cni0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1400 qdisc noqueue state UP group default qlen 1000
link/ether ae:27:5f:22:d2:18 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 10.244.0.1/24 brd 10.244.0.255 scope global cni0
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
5: veth9b446119@if3: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1400 qdisc noqueue master cni0 state UP group default
link/ether 1e:50:5b:2f:68:df brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff link-netnsid 2
6: veth96d95d6c@if3: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1400 qdisc noqueue master cni0 state UP group default
link/ether 92:68:a5:7e:f2:3d brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff link-netnsid 3
44603: eth0@if44604: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1450 qdisc noqueue state UP group default
link/ether 02:42:0a:03:6e:09 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff link-netnsid 0
inet 10.3.110.9/24 brd 10.3.110.255 scope global eth0
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
44605: eth1@if44606: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state UP group default
link/ether 02:42:ac:19:00:1c brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff link-netnsid 1
inet 172.25.0.28/24 brd 172.25.0.255 scope global eth1
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
root@controlplane:~#
What is the MAC address of the interface on the master node?
root@controlplane:~# ip link show eth0
44603: eth0@if44604: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1450 qdisc noqueue state UP mode DEFAULT group default
link/ether 02:42:0a:03:6e:09 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff link-netnsid 0
root@controlplane:~#
root@controlplane:~# arp
Address HWtype HWaddress Flags Mask Iface
10.3.110.4 ether 02:42:0a:03:6e:04 C eth0
10.244.0.2 ether d2:cc:5a:40:2c:52 C cni0
10.244.1.0 ether 7e:18:9a:b8:f0:88 CM flannel.1
10.3.110.11 ether 02:42:0a:03:6e:0a C eth0
10.3.110.13 ether 02:42:0a:03:6e:0d C eth0
10.3.110.7 ether 02:42:0a:03:6e:07 C eth0
10.244.0.3 ether 6e:50:0b:a2:84:d1 C cni0
10.3.110.10 ether 02:42:0a:03:6e:0a C eth0
k8-multi-node-ttyd-1-20 ether 02:42:0a:03:6e:0c C eth0
172.25.0.1 ether 02:42:64:28:fa:49 C eth1
root@controlplane:~#
root@controlplane:~# arp controlplane
controlplane (10.3.110.9) -- no entry
root@controlplane:~# arp node01
Address HWtype HWaddress Flags Mask Iface
10.3.110.11 ether 02:42:0a:03:6e:0a C eth0
root@controlplane:~#
root@controlplane:~# ssh node01
root@node01:~# arp
Address HWtype HWaddress Flags Mask Iface
10.3.110.4 ether 02:42:0a:03:6e:04 C eth0
10.3.110.8 ether 02:42:0a:03:6e:0d C eth0
k8-multi-node-ttyd-1-20 ether 02:42:0a:03:6e:09 C eth0
10.244.0.0 ether ce:f4:d8:2e:e4:ae CM flannel.1
172.17.0.1 ether 02:42:6e:67:3c:7a C eth1
10.3.110.13 ether 02:42:0a:03:6e:0d C eth0
10.3.110.10 ether 02:42:0a:03:6e:0a C eth0
root@node01:~#
root@node01:~# arp controlplane
Address HWtype HWaddress Flags Mask Iface
10.3.110.8 ether 02:42:0a:03:6e:0d C eth0
root@node01:~#
Docker is container runtime What is the interface/bridge created by Docker on this host?
root@controlplane:~# ip link
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
2: docker0: <NO-CARRIER,BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state DOWN mode DEFAULT group default
link/ether 02:42:1b:24:29:2c brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
3: flannel.1: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1400 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN mode DEFAULT group default
link/ether ce:f4:d8:2e:e4:ae brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
4: cni0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1400 qdisc noqueue state UP mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000
link/ether ae:27:5f:22:d2:18 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
5: veth9b446119@if3: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1400 qdisc noqueue master cni0 state UP mode DEFAULT group default
link/ether 1e:50:5b:2f:68:df brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff link-netnsid 2
6: veth96d95d6c@if3: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1400 qdisc noqueue master cni0 state UP mode DEFAULT group default
link/ether 92:68:a5:7e:f2:3d brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff link-netnsid 3
44603: eth0@if44604: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1450 qdisc noqueue state UP mode DEFAULT group default
link/ether 02:42:0a:03:6e:09 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff link-netnsid 0
44605: eth1@if44606: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state UP mode DEFAULT group default
link/ether 02:42:ac:19:00:1c brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff link-netnsid 1
root@controlplane:~#
root@controlplane:~# ip link show docker0
2: docker0: <NO-CARRIER,BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state DOWN mode DEFAULT group default
link/ether 02:42:1b:24:29:2c brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
root@controlplane:~#
If you were to ping google from the master node, which route does it take?
What is the IP address of the Default Gateway?
root@controlplane:~# ip route show
default via 172.25.0.1 dev eth1
10.3.110.0/24 dev eth0 proto kernel scope link src 10.3.110.9
10.244.0.0/24 dev cni0 proto kernel scope link src 10.244.0.1
10.244.1.0/24 via 10.244.1.0 dev flannel.1 onlink
172.12.0.0/24 dev docker0 proto kernel scope link src 172.12.0.1 linkdown
172.25.0.0/24 dev eth1 proto kernel scope link src 172.25.0.28
root@controlplane:~#
root@controlplane:~# ip route show default
default via 172.25.0.1 dev eth1
root@controlplane:~#
pod_networking
Requirements for POD networking:
-------------------------------------------->
There is no proper networking solution available in kubernetes as of now.
1. Every pod should have an unique IP address.
2. Every pod should be able to communicate with every other pod in the same node.
3. Every pod should be able to communicate with every other pod in other nodes without NAT.
There are Mnay networking solutions available to achieve this pod networking model. like
weaveworks, flannel, ciliumm, calico, vmwareNSX etc...
Manually solving the networking problem using network-namespaces we already used below commands:
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------>
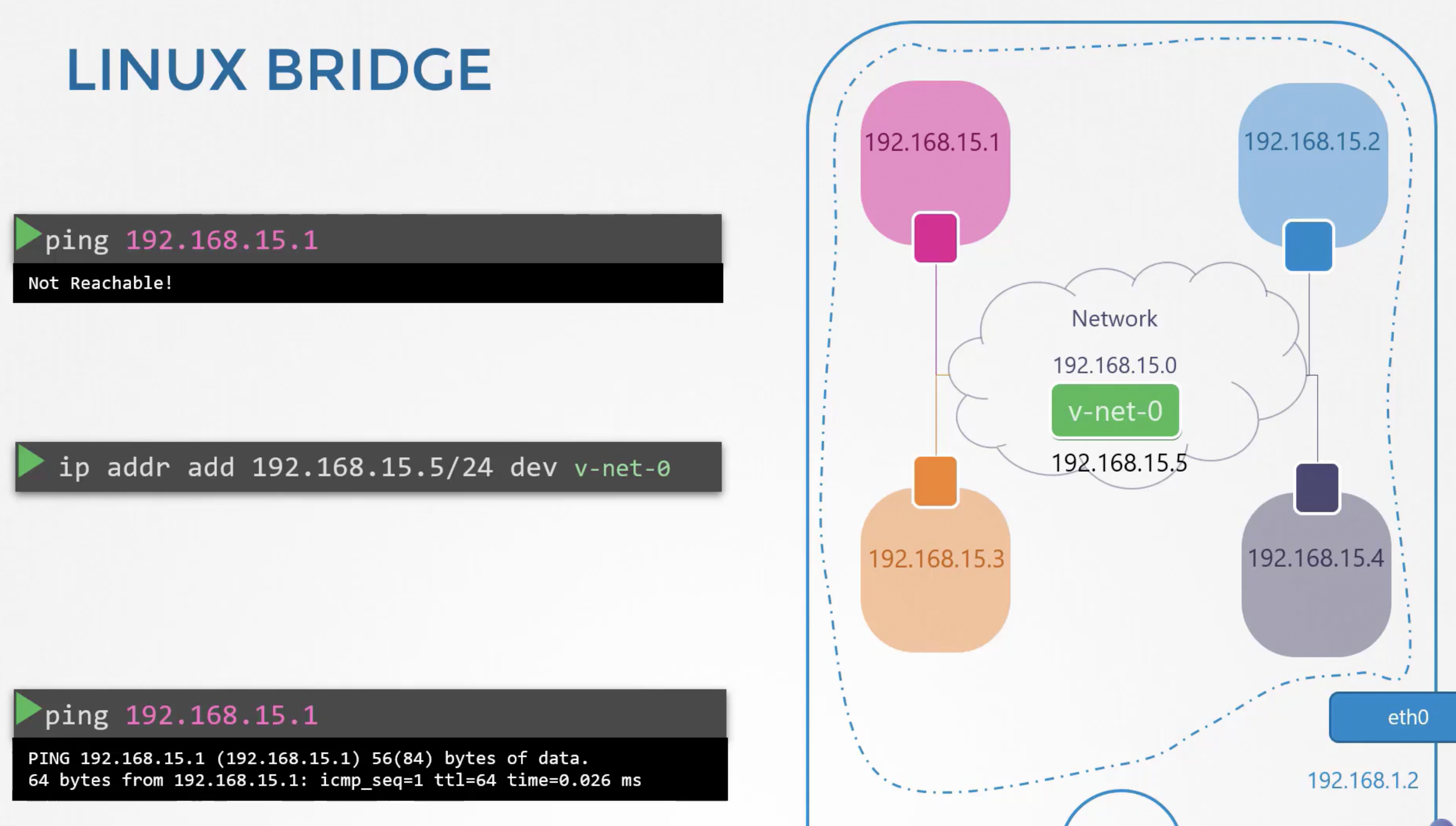
"1. ip link add v-net-0 type bridge"
"2. ip link set dev v-net-0 up"
"3. ip addr add 192.168.15.5/24 dev v-net-0"
"4. ip link add veth-red type veth peer name veth-red-br"
"5. ip link set veth-red netns red"
"6. ip -n red addr add 192.168.15.1 dev veth-red"
"7. ip -n red link set veth-red up"
"8. ip link set veth-red-br master v-net-0"
"9. ip netns exec blue ip route add 192.168.1.0/24 via 192.168.25.5"
"10. iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -s 192.168.15.0/24 -j MASQUERADE"
Those are the commands we used in plain network namespace...where as in kubernetes to solve same problem we have CNI...i.e.
we have third party networking solutions like weaveworks, flannel, calico which meets CNI standards.
pass the CNI scripts to kubelet ...
in kubelet.service file:
-------------------------------->
--cni-conf-dir=/etc/cni/net.d
--cni-bin-dir=/etc/cni/bin
each time a container is created in the pod the CNI sctipt executes ./net-scripts.sh add <container> <namespace>
CNI_k8s
Bridging
Natting
Masquerading
CNI
CNI plugins
1. container runtime must create network namespaces.
2. identify the nwetwork the container must attach to.
3. Container runtime to invoke network plugin(bridge) when container is added.
4. Container runtime to invoke Network plugin(bridge) when contiNER is Deleted.
CNI plugin must configure with kubelet in each node of the cluster.
kubelet.service:
--------------------->
ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/kubelet \\
...
--network-plugin=cni \\
--cni-bin-dir=/opt/cni/bin \\
--cni-conf-dir=/etc/cni/net.d \\
...
MacBook-Pro:certified_kubernetes_administrator bharathdasaraju$ docker ps
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
15a6fd66b44e gcr.io/k8s-minikube/kicbase:v0.0.22 "/usr/local/bin/entr…" 6 days ago Up About a minute 127.0.0.1:32772->22/tcp, 127.0.0.1:32771->2376/tcp, 127.0.0.1:32770->5000/tcp, 127.0.0.1:32769->8443/tcp, 127.0.0.1:32768->32443/tcp minikube
MacBook-Pro:certified_kubernetes_administrator bharathdasaraju$ docker exec -it 15a6fd66b44e bash
root@minikube:/# ps auxwww | grep -i "kubelet "
root 1003 12.6 4.5 1942524 92408 ? Ssl 06:34 0:08 /var/lib/minikube/binaries/v1.20.2/kubelet --bootstrap-kubeconfig=/etc/kubernetes/bootstrap-kubelet.conf --config=/var/lib/kubelet/config.yaml --container-runtime=docker --hostname-override=minikube --kubeconfig=/etc/kubernetes/kubelet.conf --node-ip=192.168.49.2
root 3819 0.0 0.0 3436 724 pts/1 S+ 06:35 0:00 grep --color=auto -i kubelet
root@minikube:/#
CNI_Weave
Weave CNI Plugin:
--------------------->
Weave creates its own bridge on the nodes and names it weave.
Then assigns IP address to each network.
Weaves can be deployed as services(or)daemonsets in each node.
kubectl apply -f "https://cloud.weave.works/k8s/net?k8s-version=$(kubectl version | base64 | tr -d '\n')"
MacBook-Pro:8.Networking bharathdasaraju$ kubectl apply -f "https://cloud.weave.works/k8s/net?k8s-version=$(kubectl version | base64 | tr -d '\n')"
serviceaccount/weave-net created
clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/weave-net created
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/weave-net created
role.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/weave-net created
rolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/weave-net created
daemonset.apps/weave-net created
MacBook-Pro:8.Networking bharathdasaraju$
MacBook-Pro:8.Networking bharathdasaraju$ kubectl get all -n kube-system | grep -i weave
pod/weave-net-7p8fq 2/2 Running 1 2m46s
daemonset.apps/weave-net 1 1 1 1 1 <none> 2m46s
MacBook-Pro:8.Networking bharathdasaraju$
CNI_weavelabs
kubectl apply -f "https://cloud.weave.works/k8s/net?k8s-version=$(kubectl version | base64 | tr -d '\n')"
Inspect the kubelet service and identify the network plugin configured for Kubernetes.
root@controlplane:/etc/kubernetes/manifests# ps -eaf | grep -i "kubelet "
root 4791 1 0 07:20 ? 00:00:17 /usr/bin/kubelet --bootstrap-kubeconfig=/etc/kubernetes/bootstrap-kubelet.conf --kubeconfig=/etc/kubernetes/kubelet.conf --config=/var/lib/kubelet/config.yaml --network-plugin=cni --pod-infra-container-image=k8s.gcr.io/pause:3.2
root 10360 9757 0 07:26 pts/0 00:00:00 grep --color=auto -i kubelet
root@controlplane:/etc/kubernetes/manifests#
root@controlplane:/etc/kubernetes/manifests# ps -eaf | grep -i "kubelet " | grep --color "network-plugin"
root 4791 1 0 07:20 ? 00:00:19 /usr/bin/kubelet --bootstrap-kubeconfig=/etc/kubernetes/bootstrap-kubelet.conf --kubeconfig=/etc/kubernetes/kubelet.conf --config=/var/lib/kubelet/config.yaml --network-plugin=cni --pod-infra-container-image=k8s.gcr.io/pause:3.2
root@controlplane:/etc/kubernetes/manifests#
/opt/cni/bin
root@controlplane:/etc/systemd/system/kubelet.service.d# cd /opt/cni/bin
root@controlplane:/opt/cni/bin# ls -rtlh
total 69M
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 4.0M May 13 2020 bandwidth
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 5.7M May 13 2020 firewall
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 3.0M May 13 2020 flannel
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 3.3M May 13 2020 sbr
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 3.8M May 13 2020 portmap
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 3.3M May 13 2020 tuning
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 4.5M May 13 2020 bridge
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 4.0M May 13 2020 host-device
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 4.2M May 13 2020 ipvlan
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 3.1M May 13 2020 loopback
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 4.2M May 13 2020 macvlan
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 4.4M May 13 2020 ptp
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 4.2M May 13 2020 vlan
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 12M May 13 2020 dhcp
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 2.8M May 13 2020 static
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 3.5M May 13 2020 host-local
root@controlplane:/opt/cni/bin#
root@controlplane:/etc/cni/net.d# pwd
/etc/cni/net.d
root@controlplane:/etc/cni/net.d# cat 10-flannel.conflist
{
"name": "cbr0",
"cniVersion": "0.3.1",
"plugins": [
{
"type": "flannel",
"delegate": {
"hairpinMode": true,
"isDefaultGateway": true
}
},
{
"type": "portmap",
"capabilities": {
"portMappings": true
}
}
]
}
root@controlplane:/etc/cni/net.d#
Deploy_network
kubectl apply -f "https://cloud.weave.works/k8s/net?k8s-version=$(kubectl version | base64 | tr -d '\n')"
kubectl apply -f "https://cloud.weave.works/k8s/net?k8s-version=$(kubectl version | base64 | tr -d '\n')&env.IPALLOC_VERSION=10.50.0.0/16"
MacBook-Pro:8.Networking bharathdasaraju$ kubectl version | tr -d '\n'
Client Version: version.Info{Major:"1", Minor:"19", GitVersion:"v1.19.3", GitCommit:"1e11e4a2108024935ecfcb2912226cedeafd99df", GitTreeState:"clean", BuildDate:"2020-10-14T12:50:19Z", GoVersion:"go1.15.2", Compiler:"gc", Platform:"darwin/amd64"}Server Version: version.Info{Major:"1", Minor:"20", GitVersion:"v1.20.2", GitCommit:"faecb196815e248d3ecfb03c680a4507229c2a56", GitTreeState:"clean", BuildDate:"2021-01-13T13:20:00Z", GoVersion:"go1.15.5", Compiler:"gc", Platform:"linux/amd64"}
MacBook-Pro:8.Networking bharathdasaraju$
Deploy weave-net networking solution to the cluster.
Replace the default IP address and subnet of weave-net to the 10.50.0.0/16.
Please check the official weave installation and configuration guide which is available at the top right panel.
1.https://www.weave.works/docs/net/latest/kubernetes/kube-addon/#-changing-configuration-options
2. https://www.weave.works/docs/net/latest/kubernetes/kube-addon/#-installation
Solution:
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------>
By default, the range of IP addresses and the subnet used by weave-net is 10.32.0.0/12 and
its overlapping with the host system IP addresses.
To know the host system IP address by running ip a
root@controlplane:~# ip a
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
2: docker0: <NO-CARRIER,BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state DOWN group default
link/ether 02:42:f0:0f:ae:f6 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 172.12.0.1/24 brd 172.12.0.255 scope global docker0
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
3: datapath: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1376 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1000
link/ether 2e:12:df:d1:7a:b2 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
5: weave: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1376 qdisc noqueue state UP group default qlen 1000
link/ether 42:a3:19:0f:16:3c brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 10.50.0.1/16 brd 10.50.255.255 scope global weave
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
24838: eth0@if24839: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1450 qdisc noqueue state UP group default
link/ether 02:42:0a:0b:38:06 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff link-netnsid 0
inet 10.11.56.6/24 brd 10.11.56.255 scope global eth0
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
7: vethwe-datapath@vethwe-bridge: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1376 qdisc noqueue master datapath state UP group default
link/ether 6a:da:9e:62:c0:5d brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
8: vethwe-bridge@vethwe-datapath: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1376 qdisc noqueue master weave state UP group default
link/ether 96:e2:1f:41:bf:de brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
24840: eth1@if24841: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state UP group default
link/ether 02:42:ac:11:00:3e brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff link-netnsid 1
inet 172.17.0.62/16 brd 172.17.255.255 scope global eth1
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
9: vxlan-6784: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65535 qdisc noqueue master datapath state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1000
link/ether 52:98:c1:8c:d9:9c brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
11: vethweplf48374a@if10: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1376 qdisc noqueue master weave state UP group default
link/ether 92:f2:38:04:21:af brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff link-netnsid 2
13: vethwepl708f939@if12: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1376 qdisc noqueue master weave state UP group default
link/ether 62:b4:86:59:28:6d brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff link-netnsid 3
root@controlplane:~#
If we deploy a weave manifest file directly without changing the default IP addresses
it will overlap with the host system IP addresses and as a result,
its weave pods will go into an Error or CrashLoopBackOff state
root@controlplane:~# kubectl get po -n kube-system | grep weave
weave-net-6mckb 1/2 CrashLoopBackOff 6 6m46s
If we will go more deeper and inspect the logs then we can clearly see the issue :-
root@controlplane:~# kubectl logs -n kube-system weave-net-6mckb -c weave
Network 10.32.0.0/12 overlaps with existing route 10.40.56.0/24 on host
So we need to change the default IP address by adding
&env.IPALLOC_RANGE=10.50.0.0/16 option at the end of the manifest file.
It should be look like as follows :-
kubectl apply -f "https://cloud.weave.works/k8s/net?k8s-version=$(kubectl version | base64 | tr -d '\n')&env.IPALLOC_RANGE=10.50.0.0/16"
kubectl apply -f "https://cloud.weave.works/k8s/net?k8s-version=$(kubectl version | base64 | tr -d '\n')&env.IPALLOC_RANGE=10.50.0.0/16"
kubectl apply -f "https://cloud.weave.works/k8s/net?k8s-version=$(kubectl version | base64 | tr -d '\n')&env.IPALLOC_RANGE=10.50.0.0/16"
root@controlplane:~# kubectl apply -f "https://cloud.weave.works/k8s/net?k8s-version=$(kubectl version | base64 | tr -d '\n')&env.IPALLOC_RANGE=10.50.0.0/16"
serviceaccount/weave-net created
clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/weave-net created
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/weave-net created
role.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/weave-net created
rolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/weave-net created
daemonset.apps/weave-net created
root@controlplane:~#
root@controlplane:~# kubectl get pods -n kube-system
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
coredns-74ff55c5b-lfq6t 1/1 Running 0 44m
coredns-74ff55c5b-shjds 1/1 Running 0 44m
etcd-controlplane 1/1 Running 0 44m
kube-apiserver-controlplane 1/1 Running 0 44m
kube-controller-manager-controlplane 1/1 Running 0 44m
kube-proxy-pl6br 1/1 Running 0 44m
kube-scheduler-controlplane 1/1 Running 0 44m
weave-net-vkbt9 2/2 Running 0 22s
root@controlplane:~#
IPAM_Weave
IPAM = IP Address Management(IPAM)
how are the virtual bridge networks and nodes assgined an IP Subnet and how are the pods assigned an IP. Where is this information stored.
who is responsible to make sure there are no duplicate IPs assigned.
kubectl apply -f "https://cloud.weave.works/k8s/net?k8s-version=$(kubectl version | base64 | tr -d '\n')&env.IPALLOC_RANGE=10.50.0.0/16"
kubectl apply -f "https://cloud.weave.works/k8s/net?k8s-version=$(kubectl version | base64 | tr -d '\n')&env.IPALLOC_RANGE=10.50.0.0/16"
to manage IP addresses locally CNI plugin uses two methods
"1.DHCP"
"2.host-local"
IPAM_Weavelabs
root@controlplane:~# kubectl get nodes -o wide
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION INTERNAL-IP EXTERNAL-IP OS-IMAGE KERNEL-VERSION CONTAINER-RUNTIME
controlplane Ready control-plane,master 53m v1.20.0 10.12.176.6 <none> Ubuntu 18.04.5 LTS 5.4.0-1052-gcp docker://19.3.0
node01 Ready <none> 52m v1.20.0 10.12.176.9 <none> Ubuntu 18.04.5 LTS 5.4.0-1052-gcp docker://19.3.0
root@controlplane:~#
root@controlplane:~# kubectl get nodes -o wide
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION INTERNAL-IP EXTERNAL-IP OS-IMAGE KERNEL-VERSION CONTAINER-RUNTIME
controlplane Ready control-plane,master 53m v1.20.0 10.12.176.6 <none> Ubuntu 18.04.5 LTS 5.4.0-1052-gcp docker://19.3.0
node01 Ready <none> 52m v1.20.0 10.12.176.9 <none> Ubuntu 18.04.5 LTS 5.4.0-1052-gcp docker://19.3.0
root@controlplane:~# ps aux | grep -i "kubelet"
root 3653 0.0 0.1 1103940 351196 ? Ssl 07:42 5:33 kube-apiserver --advertise-address=10.12.176.6 --allow-privileged=true --authorization-mode=Node,RBAC --client-ca-file=/etc/kubernetes/pki/ca.crt --enable-admission-plugins=NodeRestriction --enable-bootstrap-token-auth=true --etcd-cafile=/etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/ca.crt --etcd-certfile=/etc/kubernetes/pki/apiserver-etcd-client.crt --etcd-keyfile=/etc/kubernetes/pki/apiserver-etcd-client.key --etcd-servers=https://127.0.0.1:2379 --insecure-port=0 --kubelet-client-certificate=/etc/kubernetes/pki/apiserver-kubelet-client.crt --kubelet-client-key=/etc/kubernetes/pki/apiserver-kubelet-client.key --kubelet-preferred-address-types=InternalIP,ExternalIP,Hostname --proxy-client-cert-file=/etc/kubernetes/pki/front-proxy-client.crt --proxy-client-key-file=/etc/kubernetes/pki/front-proxy-client.key --requestheader-allowed-names=front-proxy-client --requestheader-client-ca-file=/etc/kubernetes/pki/front-proxy-ca.crt --requestheader-extra-headers-prefix=X-Remote-Extra- --requestheader-group-headers=X-Remote-Group --requestheader-username-headers=X-Remote-User --secure-port=6443 --service-account-issuer=https://kubernetes.default.svc.cluster.local --service-account-key-file=/etc/kubernetes/pki/sa.pub --service-account-signing-key-file=/etc/kubernetes/pki/sa.key --service-cluster-ip-range=10.96.0.0/12 --tls-cert-file=/etc/kubernetes/pki/apiserver.crt --tls-private-key-file=/etc/kubernetes/pki/apiserver.key
root 4865 0.0 0.0 4150812 85812 ? Ssl 07:42 2:54 /usr/bin/kubelet --bootstrap-kubeconfig=/etc/kubernetes/bootstrap-kubelet.conf --kubeconfig=/etc/kubernetes/kubelet.conf --config=/var/lib/kubelet/config.yaml --network-plugin=cni --pod-infra-container-image=k8s.gcr.io/pause:3.2
root 29476 0.0 0.0 11468 1100 pts/0 S+ 08:36 0:00 grep --color=auto -i kubelet
root@controlplane:~#
root@controlplane:~# kubectl get pods -n kube-system
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
coredns-74ff55c5b-4d5mc 1/1 Running 0 54m
coredns-74ff55c5b-mwjtw 1/1 Running 0 54m
etcd-controlplane 1/1 Running 0 54m
kube-apiserver-controlplane 1/1 Running 0 54m
kube-controller-manager-controlplane 1/1 Running 0 54m
kube-proxy-5tktf 1/1 Running 0 53m
kube-proxy-knlpw 1/1 Running 0 54m
kube-scheduler-controlplane 1/1 Running 0 54m
weave-net-8f8xq 2/2 Running 1 54m
weave-net-zzs6l 2/2 Running 0 53m
root@controlplane:~#
root@controlplane:/etc/cni/net.d# pwd
/etc/cni/net.d
root@controlplane:/etc/cni/net.d# ls
10-weave.conflist
root@controlplane:/etc/cni/net.d# cat 10-weave.conflist
{
"cniVersion": "0.3.0",
"name": "weave",
"plugins": [
{
"name": "weave",
"type": "weave-net",
"hairpinMode": true
},
{
"type": "portmap",
"capabilities": {"portMappings": true},
"snat": true
}
]
}
root@controlplane:/etc/cni/net.d#
root@controlplane:/etc/cni/net.d# ip addr show weave
5: weave: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1376 qdisc noqueue state UP group default qlen 1000
link/ether 06:b9:8c:8c:cc:9a brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 10.50.0.1/16 brd 10.50.255.255 scope global weave
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
root@controlplane:/etc/cni/net.d#
root@controlplane:/etc/cni/net.d# arp
Address HWtype HWaddress Flags Mask Iface
10.50.0.3 ether ae:23:0f:b1:b6:f6 C weave
10.12.176.4 ether 02:42:0a:0c:b0:04 C eth0
10.12.176.13 ether 02:42:0a:0c:b0:0d C eth0
10.12.176.7 ether 02:42:0a:0c:b0:07 C eth0
10.12.176.10 ether 02:42:0a:0c:b0:0a C eth0
k8-multi-node-weave-tty ether 02:42:0a:0c:b0:09 C eth0
172.25.0.1 ether 02:42:64:28:fa:49 C eth1
10.50.0.2 ether fa:b3:57:78:c6:ea C weave
10.12.176.8 ether 02:42:0a:0c:b0:07 C eth0
root@controlplane:/etc/cni/net.d# ip route
default via 172.25.0.1 dev eth1
10.12.176.0/24 dev eth0 proto kernel scope link src 10.12.176.6
10.50.0.0/16 dev weave proto kernel scope link src 10.50.0.1
172.12.0.0/24 dev docker0 proto kernel scope link src 172.12.0.1 linkdown
172.25.0.0/24 dev eth1 proto kernel scope link src 172.25.0.24
root@controlplane:/etc/cni/net.d#
root@controlplane:/etc/cni/net.d# arp
Address HWtype HWaddress Flags Mask Iface
10.50.0.3 ether ae:23:0f:b1:b6:f6 C weave
10.12.176.4 ether 02:42:0a:0c:b0:04 C eth0
10.12.176.13 ether 02:42:0a:0c:b0:0d C eth0
10.12.176.7 ether 02:42:0a:0c:b0:07 C eth0
10.12.176.10 ether 02:42:0a:0c:b0:0a C eth0
k8-multi-node-weave-tty ether 02:42:0a:0c:b0:09 C eth0
172.25.0.1 ether 02:42:64:28:fa:49 C eth1
10.50.0.2 ether fa:b3:57:78:c6:ea C weave
10.12.176.8 ether 02:42:0a:0c:b0:07 C eth0
root@controlplane:/etc/cni/net.d# ip route
default via 172.25.0.1 dev eth1
10.12.176.0/24 dev eth0 proto kernel scope link src 10.12.176.6
10.50.0.0/16 dev weave proto kernel scope link src 10.50.0.1
172.12.0.0/24 dev docker0 proto kernel scope link src 172.12.0.1 linkdown
172.25.0.0/24 dev eth1 proto kernel scope link src 172.25.0.24
root@controlplane:/etc/cni/net.d#
kubeclt exec -it pod-webapp
ip route
Service_Networking
ClusterIP: accessible only within the cluster.
NodePort: can also accessible from outside
when a service is created it is assigned an IP Address from a pre-defined range.
the "kube-proxy" component running on each node, gets that IP Address and creates forwarding rule on each node of the cluster using IPAddress and Port.
"kube-proxy" uses "iptables" to create forwarding rules.
iptables -L -t nat
/var/log/kube-proxy.log
Service_Networkinglabs
What network range are the nodes in the cluster part of?
ip addr and look at the IP address assigned to the eth0 interfaces. Derive network range from that.
root@controlplane:~# apt-get install -y ipcalc
Reading package lists... Done
Building dependency tree
Reading state information... Done
ipcalc is already the newest version (0.41-5).
0 upgraded, 0 newly installed, 0 to remove and 0 not upgraded.
root@controlplane:~#
root@controlplane:~# ip a | grep eth0
4227: eth0@if4228: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1450 qdisc noqueue state UP group default
inet 10.15.219.6/24 brd 10.15.219.255 scope global eth0
root@controlplane:~# ipcalc -b 10.15.219.6/24
Address: 10.15.219.6
Netmask: 255.255.255.0 = 24
Wildcard: 0.0.0.255
=>
Network: 10.15.219.0/24
HostMin: 10.15.219.1
HostMax: 10.15.219.254
Broadcast: 10.15.219.255
Hosts/Net: 254 Class A, Private Internet
root@controlplane:~#
What is the range of IP addresses configured for PODs on this cluster?
# kubectl logs weave-net-627nk weave -n kube-system
root@controlplane:~# kubectl logs weave-net-627nk -n kube-system
error: a container name must be specified for pod weave-net-627nk, choose one of: [weave weave-npc] or one of the init containers: [weave-init]
root@controlplane:~# kubectl logs weave-net-627nk weave -n kube-system
DEBU: 2021/09/27 08:54:52.452110 [kube-peers] Checking peer "86:d2:8d:82:da:47" against list &{[]}
Peer not in list; removing persisted data
INFO: 2021/09/27 08:54:52.774655 Command line options: map[conn-limit:200 datapath:datapath db-prefix:/weavedb/weave-net docker-api: expect-npc:true http-addr:127.0.0.1:6784 ipalloc-init:consensus=0 ipalloc-range:10.50.0.0/16 metrics-addr:0.0.0.0:6782 name:86:d2:8d:82:da:47 nickname:controlplane no-dns:true no-masq-local:true port:6783]
INFO: 2021/09/27 08:54:52.774804 weave 2.8.1
INFO: 2021/09/27 08:54:54.268379 Bridge type is bridged_fastdp
INFO: 2021/09/27 08:54:54.268428 Communication between peers is unencrypted.
INFO: 2021/09/27 08:54:54.273996 Our name is 86:d2:8d:82:da:47(controlplane)
INFO: 2021/09/27 08:54:54.274073 Launch detected - using supplied peer list: []
INFO: 2021/09/27 08:54:54.274156 Using "no-masq-local" LocalRangeTracker
INFO: 2021/09/27 08:54:54.274172 Checking for pre-existing addresses on weave bridge
INFO: 2021/09/27 08:54:54.276122 [allocator 86:d2:8d:82:da:47] No valid persisted data
INFO: 2021/09/27 08:54:54.284607 [allocator 86:d2:8d:82:da:47] Initialising via deferred consensus
INFO: 2021/09/27 08:54:54.284740 Sniffing traffic on datapath (via ODP)
INFO: 2021/09/27 08:54:54.334151 Listening for HTTP control messages on 127.0.0.1:6784
INFO: 2021/09/27 08:54:54.334441 Listening for metrics requests on 0.0.0.0:6782
INFO: 2021/09/27 08:54:54.468655 Error checking version: Get "https://checkpoint-api.weave.works/v1/check/weave-net?arch=amd64&flag_docker-version=none&flag_kernel-version=5.4.0-1052-gcp&os=linux&signature=gcF912ffmo8YREblTPlm3cNoSXNxl8a63a%2F%2BwEt4%2B4w%3D&version=2.8.1": dial tcp: lookup checkpoint-api.weave.works on 10.96.0.10:53: write udp 172.17.0.81:37204->10.96.0.10:53: write: operation not permitted
INFO: 2021/09/27 08:54:54.736502 [kube-peers] Added myself to peer list &{[{86:d2:8d:82:da:47 controlplane}]}
DEBU: 2021/09/27 08:54:54.747796 [kube-peers] Nodes that have disappeared: map[]
INFO: 2021/09/27 08:54:54.774377 Assuming quorum size of 1
INFO: 2021/09/27 08:54:54.774565 adding entry 10.50.0.0/16 to weaver-no-masq-local of 0
INFO: 2021/09/27 08:54:54.774591 added entry 10.50.0.0/16 to weaver-no-masq-local of 0
10.50.0.1
DEBU: 2021/09/27 08:54:54.948924 registering for updates for node delete events
INFO: 2021/09/27 08:55:24.325962 ->[10.15.219.9:51035] connection accepted
INFO: 2021/09/27 08:55:24.327492 ->[10.15.219.9:51035|7a:0a:e1:78:3a:84(node01)]: connection ready; using protocol version 2
INFO: 2021/09/27 08:55:24.327736 overlay_switch ->[7a:0a:e1:78:3a:84(node01)] using fastdp
INFO: 2021/09/27 08:55:24.327778 ->[10.15.219.9:51035|7a:0a:e1:78:3a:84(node01)]: connection added (new peer)
INFO: 2021/09/27 08:55:24.428675 ->[10.15.219.9:51035|7a:0a:e1:78:3a:84(node01)]: connection fully established
INFO: 2021/09/27 08:55:24.430068 sleeve ->[10.15.219.9:6783|7a:0a:e1:78:3a:84(node01)]: Effective MTU verified at 1388
INFO: 2021/09/27 08:55:25.429246 adding entry 10.50.0.0/17 to weaver-no-masq-local of 0
INFO: 2021/09/27 08:55:25.429292 added entry 10.50.0.0/17 to weaver-no-masq-local of 0
INFO: 2021/09/27 08:55:25.430688 adding entry 10.50.128.0/18 to weaver-no-masq-local of 0
INFO: 2021/09/27 08:55:25.430747 added entry 10.50.128.0/18 to weaver-no-masq-local of 0
INFO: 2021/09/27 08:55:25.431762 deleting entry 10.50.0.0/16 from weaver-no-masq-local of 0
INFO: 2021/09/27 08:55:25.431799 deleted entry 10.50.0.0/16 from weaver-no-masq-local of 0
INFO: 2021/09/27 08:55:25.493874 Discovered remote MAC 7a:0a:e1:78:3a:84 at 7a:0a:e1:78:3a:84(node01)
root@controlplane:~#
What is the IP Range configured for the services within the cluster?
root@controlplane:~# cat /etc/kubernetes/manifests/kube-apiserver.yaml | grep cluster-ip-range
- --service-cluster-ip-range=10.96.0.0/12
root@controlplane:~#
What type of proxy is the kube-proxy configured to use?
root@controlplane:~# kubectl get all --all-namespaces | grep -i "kube-proxy"
kube-system pod/kube-proxy-4mgll 1/1 Running 0 31m
kube-system pod/kube-proxy-59dvb 1/1 Running 0 30m
kube-system daemonset.apps/kube-proxy 2 2 2 2 2 kubernetes.io/os=linux 31m
root@controlplane:~# kubectl logs kube-proxy-4mgll -n kube-system
W0927 08:54:33.945359 1 proxier.go:661] Failed to load kernel module ip_vs_wrr with modprobe. You can ignore this message when kube-proxy is running inside container without mounting /lib/modules
W0927 08:54:33.949143 1 proxier.go:661] Failed to load kernel module ip_vs_sh with modprobe. You can ignore this message when kube-proxy is running inside container without mounting /lib/modules
I0927 08:54:34.052244 1 node.go:172] Successfully retrieved node IP: 10.15.219.6
I0927 08:54:34.052321 1 server_others.go:142] kube-proxy node IP is an IPv4 address (10.15.219.6), assume IPv4 operation
W0927 08:54:34.148331 1 server_others.go:578] Unknown proxy mode "", assuming iptables proxy
I0927 08:54:34.184424 1 server_others.go:185] Using iptables Proxier.
I0927 08:54:34.249532 1 server.go:650] Version: v1.20.0
I0927 08:54:34.270712 1 conntrack.go:52] Setting nf_conntrack_max to 1179648
I0927 08:54:34.273624 1 conntrack.go:100] Set sysctl 'net/netfilter/nf_conntrack_tcp_timeout_established' to 86400
I0927 08:54:34.277353 1 config.go:315] Starting service config controller
I0927 08:54:34.277384 1 shared_informer.go:240] Waiting for caches to sync for service config
I0927 08:54:34.277433 1 config.go:224] Starting endpoint slice config controller
I0927 08:54:34.277454 1 shared_informer.go:240] Waiting for caches to sync for endpoint slice config
I0927 08:54:34.377692 1 shared_informer.go:247] Caches are synced for service config
I0927 08:54:34.377695 1 shared_informer.go:247] Caches are synced for endpoint slice config
root@controlplane:~#
root@controlplane:~# kubectl logs pod/kube-proxy-59dvb -n kube-system
W0927 08:55:14.401382 1 proxier.go:661] Failed to load kernel module ip_vs_wrr with modprobe. You can ignore this message when kube-proxy is running inside container without mounting /lib/modules
W0927 08:55:14.407380 1 proxier.go:661] Failed to load kernel module ip_vs_sh with modprobe. You can ignore this message when kube-proxy is running inside container without mounting /lib/modules
I0927 08:55:14.495137 1 node.go:172] Successfully retrieved node IP: 10.15.219.9
I0927 08:55:14.495184 1 server_others.go:142] kube-proxy node IP is an IPv4 address (10.15.219.9), assume IPv4 operation
W0927 08:55:14.679926 1 server_others.go:578] Unknown proxy mode "", assuming iptables proxy
I0927 08:55:14.817002 1 server_others.go:185] Using iptables Proxier.
I0927 08:55:14.934375 1 server.go:650] Version: v1.20.0
I0927 08:55:15.014109 1 conntrack.go:52] Setting nf_conntrack_max to 1179648
I0927 08:55:15.017569 1 conntrack.go:100] Set sysctl 'net/netfilter/nf_conntrack_tcp_timeout_established' to 86400
I0927 08:55:15.021132 1 config.go:315] Starting service config controller
I0927 08:55:15.021166 1 shared_informer.go:240] Waiting for caches to sync for service config
I0927 08:55:15.021203 1 config.go:224] Starting endpoint slice config controller
I0927 08:55:15.021223 1 shared_informer.go:240] Waiting for caches to sync for endpoint slice config
I0927 08:55:15.121378 1 shared_informer.go:247] Caches are synced for service config
I0927 08:55:15.121405 1 shared_informer.go:247] Caches are synced for endpoint slice config
root@controlplane:~#
k8sDNS
DNS Resolution within the cluster.
Kubenetes deploys a built-in DNS server by default when we setup a cluster.
if we setup Kubenetes manually then we need setup DNS server by our selves.
"for example:"
--------------------->
in "default" namespace we have
--> one pod called "test"
in "apps" namespace we have
--> one pod namely "web" and
--> a service called "web-service"
From the "test" pod we can access the "web-service" with name "web-service.apps" i.e. "service_name.namespace"
"service fully_qualified domain:" http://web-service.apps.svc.cluster.local
pod_ip: 10.244.2.5 for pod_fqdn: http://10-244-2-5.apps.pod.cluster.local
k8scoreDNS
Prior to 1.12 the DNS server called the "kube-dns"
with version 1.12 the recommended DNS server is coreDNS.
core-dns deployed as a pods in kube-sytem namespace.
./Coredns requires a config file located in /etc/coredns/Corefile
When coreDNS deployed its solution it has created a service called "kube-dns"
when ever a new pod created in its "/etc/resolv.conf" the "kube-dns service's" clusterIP gets configured.
to add the above entry is the job of kubelet(it will be done automatically)
cat /var/lib/kubelet/config.yaml
---------------------------------------->
...
clusterDNS:
- 10.96.0.10
clusterDomain: cluster.local
k8scoreDNSlabs
root@controlplane:~# kubectl get pods -n kube-system
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
coredns-74ff55c5b-9rj2x 1/1 Running 0 10m
coredns-74ff55c5b-vdgtz 1/1 Running 0 10m
etcd-controlplane 1/1 Running 0 11m
kube-apiserver-controlplane 1/1 Running 0 11m
kube-controller-manager-controlplane 1/1 Running 0 11m
kube-flannel-ds-z2dfx 1/1 Running 0 10m
kube-proxy-rbb8b 1/1 Running 0 10m
kube-scheduler-controlplane 1/1 Running 0 11m
root@controlplane:~#
root@controlplane:~# kubectl get svc -n kube-system -o wide
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE SELECTOR
kube-dns ClusterIP 10.96.0.10 <none> 53/UDP,53/TCP,9153/TCP 12m k8s-app=kube-dns
root@controlplane:~#
root@controlplane:~# kubectl describe deployment.apps/coredns -n kube-system | grep -iC2 "Corefile"
Args:
-conf
/etc/coredns/Corefile
Limits:
memory: 170Mi
root@controlplane:~#
How is the Corefile passed in to the CoreDNS POD?
root@controlplane:~# kubectl get cm -n kube-system
NAME DATA AGE
coredns 1 27m
extension-apiserver-authentication 6 27m
kube-flannel-cfg 2 27m
kube-proxy 2 27m
kube-root-ca.crt 1 26m
kubeadm-config 2 27m
kubelet-config-1.20 1 27m
root@controlplane:~#
What is the root domain/zone configured for this kubernetes cluster?
root@controlplane:~# kubectl describe cm coredns -n kube-system
Name: coredns
Namespace: kube-system
Labels: <none>
Annotations: <none>
Data
====
Corefile:
----
.:53 {
errors
health {
lameduck 5s
}
ready
kubernetes cluster.local in-addr.arpa ip6.arpa {
pods insecure
fallthrough in-addr.arpa ip6.arpa
ttl 30
}
prometheus :9153
forward . /etc/resolv.conf {
max_concurrent 1000
}
cache 30
loop
reload
loadbalance
}
Events: <none>
root@controlplane:~#
root@controlplane:~# kubectl get pods -n default
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
hr 1/1 Running 0 19m
simple-webapp-1 1/1 Running 0 19m
simple-webapp-122 1/1 Running 0 19m
test 1/1 Running 0 19m
root@controlplane:~# kubectl get pods -n payroll
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
web 1/1 Running 0 19m
root@controlplane:~#
root@controlplane:~# kubectl get svc -n default
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
kubernetes ClusterIP 10.96.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 30m
test-service NodePort 10.96.151.101 <none> 80:30080/TCP 21m
web-service ClusterIP 10.103.4.192 <none> 80/TCP 21m
root@controlplane:~# kubectl get svc -n payroll
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
web-service ClusterIP 10.105.43.19 <none> 80/TCP 21m
root@controlplane:~#
We just deployed a web server - webapp - that accesses a database mysql - server.
However the web server is failing to connect to the database server. Troubleshoot and fix the issue.
They could be in different namespaces. First locate the applications.
The web server interface can be seen by clicking the tab Web Server at the top of your terminal.
root@controlplane:~# kubectl get pods,svc -n default
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/hr 1/1 Running 0 24m
pod/simple-webapp-1 1/1 Running 0 24m
pod/simple-webapp-122 1/1 Running 0 24m
pod/test 1/1 Running 0 24m
pod/webapp-84ffb6ddff-kqkxl 1/1 Running 0 94s
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/kubernetes ClusterIP 10.96.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 33m
service/test-service NodePort 10.96.151.101 <none> 80:30080/TCP 24m
service/web-service ClusterIP 10.103.4.192 <none> 80/TCP 24m
service/webapp-service NodePort 10.109.186.109 <none> 8080:30082/TCP 93s
root@controlplane:~#
root@controlplane:~# kubectl get pods,svc -n payroll
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/mysql 1/1 Running 0 108s
pod/web 1/1 Running 0 24m
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/mysql ClusterIP 10.110.240.0 <none> 3306/TCP 108s
service/web-service ClusterIP 10.105.43.19 <none> 80/TCP 24m
root@controlplane:~#
root@controlplane:~# kubectl get deploy
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
webapp 1/1 1 1 3m23s
root@controlplane:~# kubectl describe deploy webapp
Name: webapp
Namespace: default
CreationTimestamp: Tue, 28 Sep 2021 00:53:34 +0000
Labels: name=webapp
Annotations: deployment.kubernetes.io/revision: 1
Selector: name=webapp
Replicas: 1 desired | 1 updated | 1 total | 1 available | 0 unavailable
StrategyType: RollingUpdate
MinReadySeconds: 0
RollingUpdateStrategy: 25% max unavailable, 25% max surge
Pod Template:
Labels: name=webapp
Containers:
simple-webapp-mysql:
Image: mmumshad/simple-webapp-mysql
Port: 8080/TCP
Host Port: 0/TCP
Environment:
DB_Host: mysql
DB_User: root
DB_Password: paswrd
Mounts: <none>
Volumes: <none>
Conditions:
Type Status Reason
---- ------ ------
Available True MinimumReplicasAvailable
Progressing True NewReplicaSetAvailable
OldReplicaSets: <none>
NewReplicaSet: webapp-84ffb6ddff (1/1 replicas created)
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
Normal ScalingReplicaSet 3m35s deployment-controller Scaled up replica set webapp-84ffb6ddff to 1
root@controlplane:~#
From the hr pod nslookup the mysql service and redirect the output to a file /root/CKA/nslookup.out
oot@controlplane:~# kubectl exec -it hr -- nslookup mysql.payroll > /root/CKA/nslookup.output
root@controlplane:~# cat /root/CKA/nslookup.output
Server: 10.96.0.10
Address: 10.96.0.10#53
Name: mysql.payroll.svc.cluster.local
Address: 10.110.240.0
root@controlplane:~#
clusterIP vs NodePort -

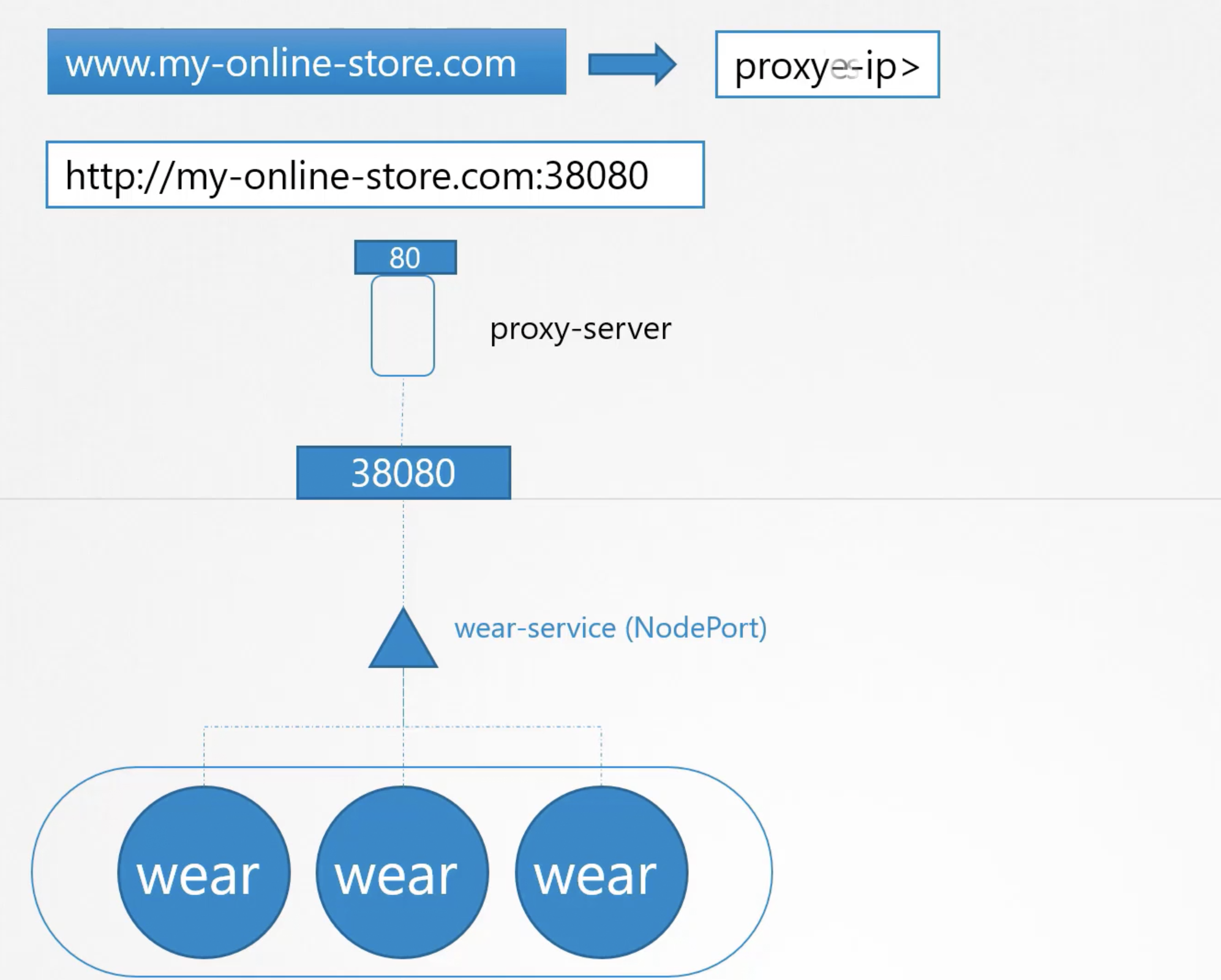
nginxconfigmap
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: nginx-confoguration
nginxingress
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx-ingress
name: nginx-ingress
spec:
ports:
- name: http
port: 80
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 80
- name: https
port: 443
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 443
selector:
app: nginx-ingress
type: NodePort
nginxingresssa
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: nginx-ingress-serviceaccount
nginx ingress controller -
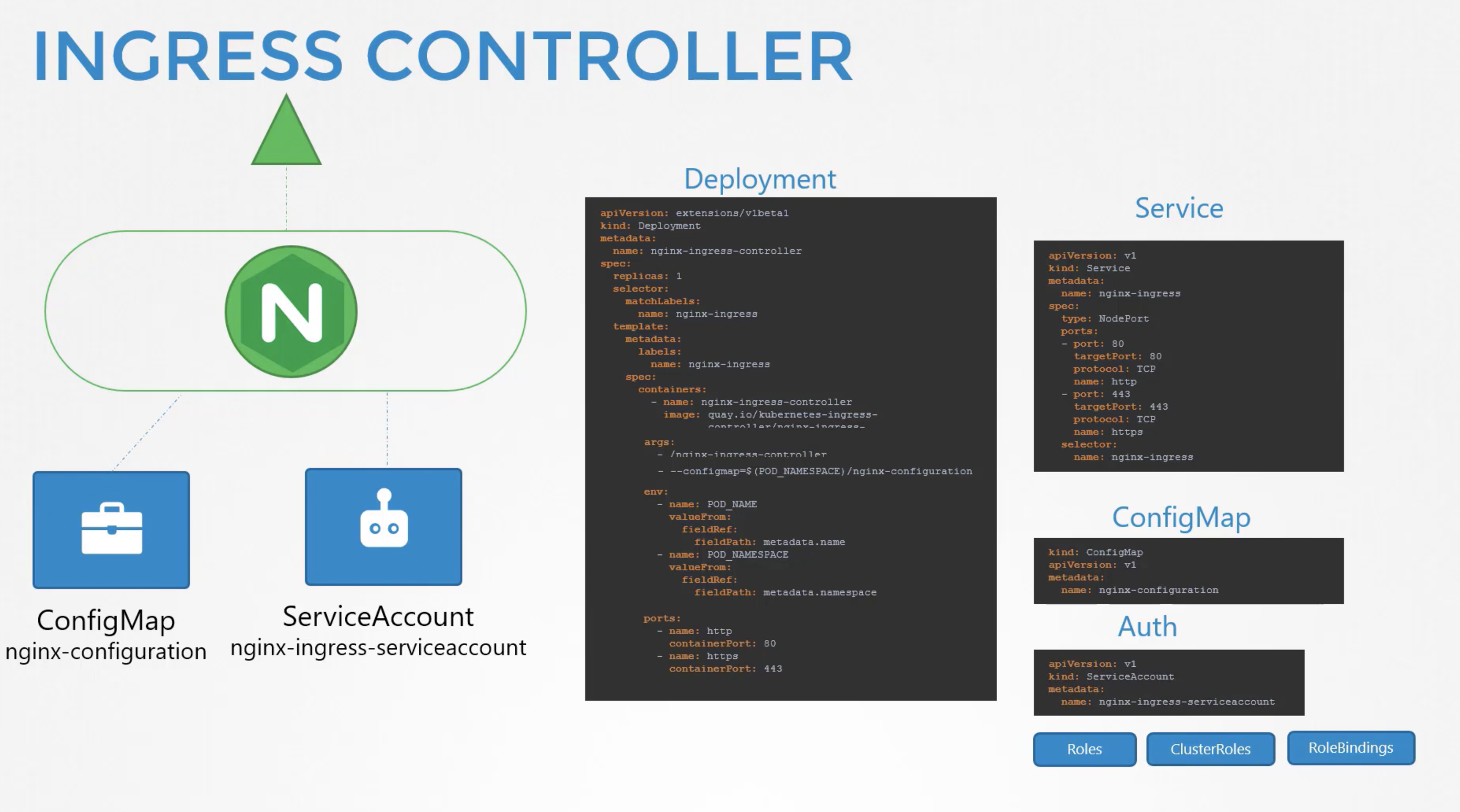
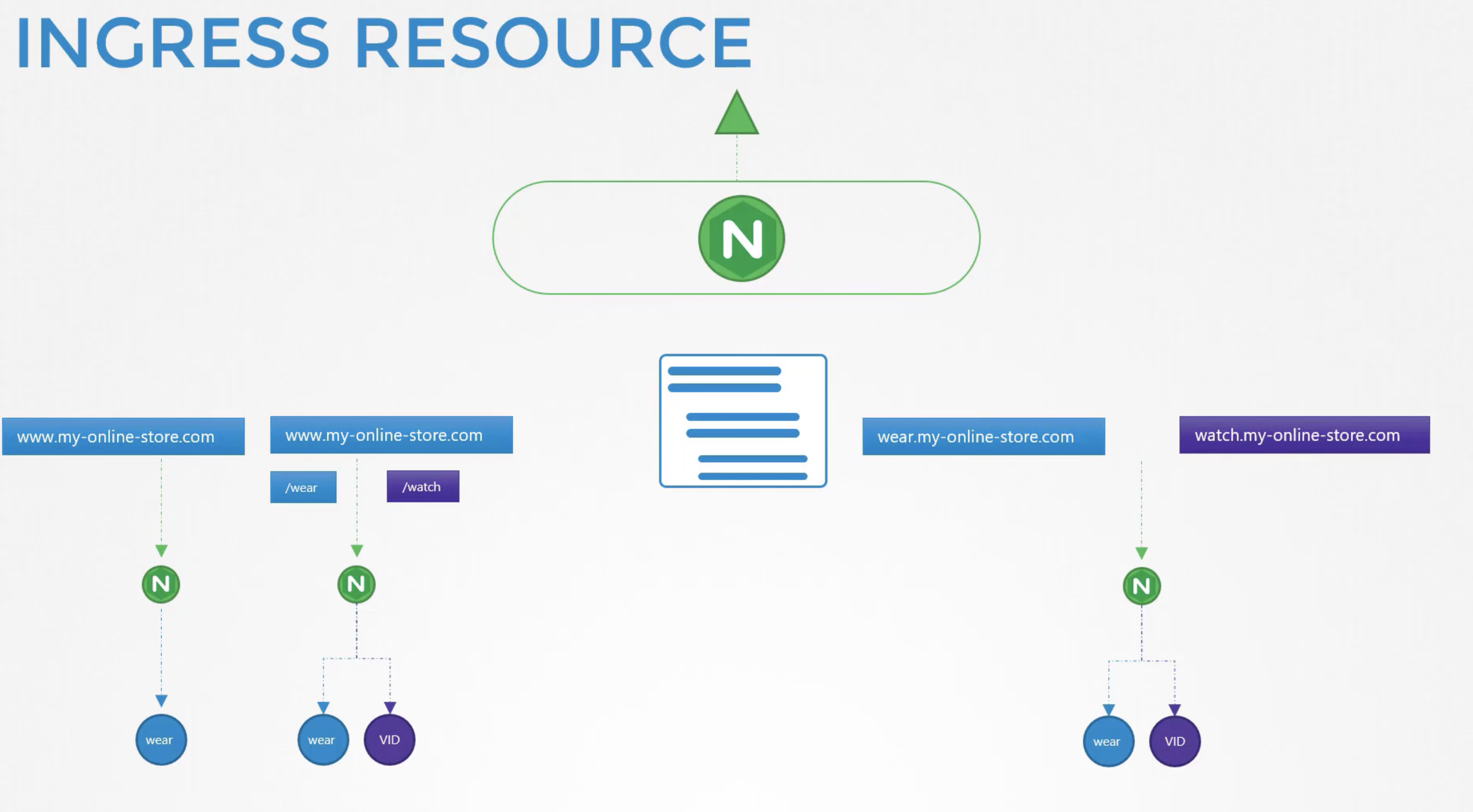
k8singress
difference between service and ingress:
---------------------------------------------->
for example: if we want to access the application on www.my-online-store.com
and if you are using GKE in google cloud... we can create serviceType LoadBalancer
if we want to access different services like videos, news, games
http://www.my-online-store.com/videos
http://www.my-online-store.com/news
http://www.my-online-store.com/games
"Ingress" helps users to access the application using a single externally accessible URL that we can configure to route different services in the cluster based on the URL path.
At the same time implement the SSL security as well.
We can think of ingress as a layer-7 loadbalancer built-in to the k8s cluster that can be configured.
Even with ingress you still need to expose it to make it accessible outside the cluster,
so we still have to either publish it as a node port or with a cloud native loadbalancer, that just onetime confgiration.
Going forward we are going to perform all our loadbalancing,auth,ssl and URL based configurations on the ingress controller.
"Without ingress":
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------->
we used a reverse-proxy (or) loadbalancing solution like nginx, haproxy, traefik.
we deployed them on k8s cluster and configure them to route traffic to other services.
configuration invloves defining URL Routes, configuring SSL certs etc...
"With ingress":
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------->
Ingress is implemented ny kubernetes in kind of the same way.
we first deploy a supported solution(nginx,haproxy,traefik) and then specify a set of rules to configure ingress.
The solution(nginx, haproxy, traefik) we deploy is called as an ingress-controller and set of rules we configure are called ingress resources.
ingress resources are created using definition files like pods,deployments etc...
kubernetes cluster does not come with an ingress-controller by default.
"Create Ingress Controller:"
------------------------------------------------------------>
There are number of solutions available for ingress those are
1. GCP http(s) loadbalancer
2. nginx
3. Contour
4. haproxy
5. traefik
6. Istion
lets take nginx. we can deploy nginx ingress controller as a deployment
MacBook-Pro:8.Networking bharathdasaraju$ kubectl create deployment nginx-ingress-controller --image=quay.io/kubernetes-ingress-controller/nginx-ingress-controller:0.21.0 --replicas=1 --dry-run=client -o yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
creationTimestamp: null
labels:
app: nginx-ingress-controller
name: nginx-ingress-controller
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx-ingress-controller
strategy: {}
template:
metadata:
creationTimestamp: null
labels:
app: nginx-ingress-controller
spec:
containers:
- image: quay.io/kubernetes-ingress-controller/nginx-ingress-controller:0.21.0
name: nginx-ingress-controller
resources: {}
status: {}
MacBook-Pro:8.Networking bharathdasaraju$
1. Add configmap for ingress controller to change confgiration settings for nginx
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: nginx-confoguration
2. add envs
3. expose ports
4. deploy a service to expose a nginx-ingress-controller
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx-ingress-controller
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx-ingress
strategy: {}
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx-ingress
spec:
containers:
- image: quay.io/kubernetes-ingress-controller/nginx-ingress-controller:0.21.0
name: nginx-ingress-controller
args:
- /nginx-ingress-controller
- --configmap=$(POD_NAMESPACE)/nginx-configuration
env:
- name: POD_NAME
valueFrom:
filedRef:
fieldPath: metadata.name
- name: POD_NAMESPACE
valueFrom:
filedRef:
fieldPath: metadata.namespace
ports:
- name: http
containerPort: 80
- name: https
containerPort: 443
MacBook-Pro:8.Networking bharathdasaraju$ kubectl create service nodeport nginx-ingress --tcp=80:80 --dry-run=client -o yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx-ingress
name: nginx-ingress
spec:
ports:
- name: http
port: 80
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 80
- name: https
port: 443
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 443
selector:
app: nginx-ingress
type: NodePort
MacBook-Pro:8.Networking bharathdasaraju$
MacBook-Pro:8.Networking bharathdasaraju$ kubectl create service nodeport nginx-ingress --tcp=80:80 --dry-run=client -o yaml > nginx-ingress-service.yaml
MacBook-Pro:8.Networking bharathdasaraju$ kubectl create sa nginx-ingress-serviceaccount --dry-run=client -o yaml > nginx-ingress-serviceaccount.yaml
MacBook-Pro:8.Networking bharathdasaraju$
For nginx-ingress-controller to work properly we need to give it to peroper roles and rolebindings by creating a "serviceaccount"
"Create Ingress Resources:"
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------->
We can specify set of rules to route traffic to differnt URLs based in URL paths.
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: ingress-wear
spec:
rules:
backend:
service:
name: wear-service
port: 80
two types of ingress rules:
--------------------------------->
Type1(URL paths):
---------------------->
http://my-online-store.com/wear
http://my-online-store.com/watch
Type2(URL names - hostnames):
------------------------------------>
http://wear.my-online-store.com
http://watch.my-online-store.com
k8singress_resourcerules
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: ingress-wear
spec:
rules:
backend:
service:
name: wear-service
port: 80
nginx ingress url-paths and url-names -
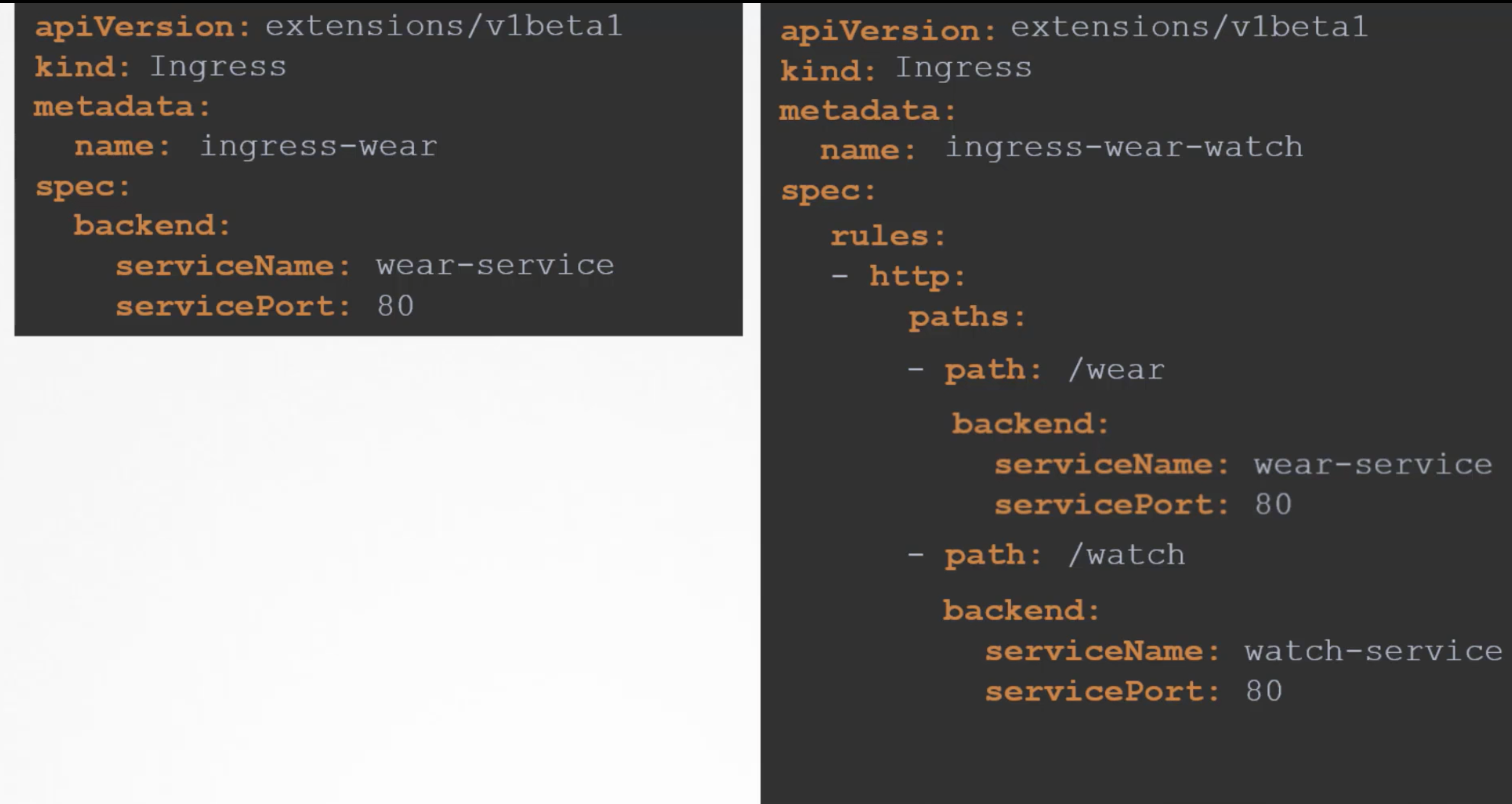


k8snginx_ingresscontroller
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx-ingress-controller
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx-ingress
strategy: {}
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx-ingress
spec:
containers:
- image: quay.io/kubernetes-ingress-controller/nginx-ingress-controller:0.21.0
name: nginx-ingress-controller
args:
- /nginx-ingress-controller
- --configmap=$(POD_NAMESPACE)/nginx-configuration
env:
- name: POD_NAME
valueFrom:
filedRef:
fieldPath: metadata.name
- name: POD_NAMESPACE
valueFrom:
filedRef:
fieldPath: metadata.namespace
ports:
- name: http
containerPort: 80
- name: https
containerPort: 443
ingress_rewrite_targets
Different ingress controllers have different options that can be used to customise the way it works.
NGINX Ingress controller has many options that can be seen here. The Rewrite target option.
Our watch app displays the video streaming webpage at http://<watch-service>:<port>/
Our wear app displays the apparel webpage at http://<wear-service>:<port>/
We must configure Ingress to achieve the below.
When user visits the URL on the left, his request should be forwarded internally to the URL on the right.
Note that the /watch and /wear URL path are what we configure on the ingress controller so we can forwarded users to the appropriate application in the backend.
The applications don’t have this URL/Path configured on them:
http://<ingress-service>:<ingress-port>/watch –> http://<watch-service>:<port>/
http://<ingress-service>:<ingress-port>/wear –> http://<wear-service>:<port>/
"Without the rewrite-target option, this is what would happen:"
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------->
http://<ingress-service>:<ingress-port>/watch –> http://<watch-service>:<port>/watch
http://<ingress-service>:<ingress-port>/wear –> http://<wear-service>:<port>/wear
Notice "watch" and "wear" at the end of the target URLs. The target applications are not configured with "/watch" or "/wear" paths.
They are different applications built specifically for their purpose,
so they dont expect "/watch" or "/wear" in the URLs. And as such the requests would fail and throw a 404 not found error.
To fix that we want to "ReWrite" the URL when the request is passed on to the watch or wear applications. We dont want to pass in the same path that user typed in.
So we specify the "rewrite-target" option.
This rewrites the URL by replacing whatever is under "rules->http->paths->path"
which happens to be "/pay" in this case with the value in rewrite-target "/"
This works just like a "search" and "replace" function.
-------------------------------------------------------------->
For example: replace(path, rewrite-target)
In our case: replace("/pay","/")
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: test-ingress
namespace: critical-space
annotations:
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/rewrite-target: /
spec:
rules:
- http:
paths:
- path: /pay
backend:
serviceName: pay-service
servicePort: 8282
ingress_rewrite_targetannotations
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: test-ingress
namespace: critical-space
annotations:
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/rewrite-target: /
spec:
rules:
- http:
paths:
- path: /pay
backend:
serviceName: pay-service
servicePort: 8282
nginxingress_networking
root@controlplane:~# kubectl get nodes -o wide
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION INTERNAL-IP EXTERNAL-IP OS-IMAGE KERNEL-VERSION CONTAINER-RUNTIME
controlplane Ready control-plane,master 7m32s v1.20.0 10.7.27.3 <none> Ubuntu 18.04.5 LTS 5.4.0-1052-gcp docker://19.3.0
root@controlplane:~#
root@controlplane:~# kubectl get deploy --all-namespaces
NAMESPACE NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
app-space default-backend 1/1 1 1 76s
app-space webapp-video 1/1 1 1 76s
app-space webapp-wear 1/1 1 1 76s
ingress-space nginx-ingress-controller 1/1 1 1 77s
kube-system coredns 2/2 2 2 8m19s
root@controlplane:~#
root@controlplane:~# kubectl get deploy -n ingress-space -o wide
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE CONTAINERS IMAGES SELECTOR
nginx-ingress-controller 1/1 1 1 107s nginx-ingress-controller quay.io/kubernetes-ingress-controller/nginx-ingress-controller:0.21.0 name=nginx-ingress
root@controlplane:~#
root@controlplane:~# kubectl get pods --all-namespaces
NAMESPACE NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
app-space default-backend-5cf9bfb9d-jv2md 1/1 Running 0 2m53s
app-space webapp-video-84f8655bd8-m5sgh 1/1 Running 0 2m53s
app-space webapp-wear-6ff9445955-sn5zq 1/1 Running 0 2m52s
ingress-space nginx-ingress-controller-697cfbd4d9-6lhdm 1/1 Running 0 2m53s
kube-system coredns-74ff55c5b-5cw7x 1/1 Running 0 9m43s
kube-system coredns-74ff55c5b-894fr 1/1 Running 0 9m43s
kube-system etcd-controlplane 1/1 Running 0 9m52s
kube-system kube-apiserver-controlplane 1/1 Running 0 9m52s
kube-system kube-controller-manager-controlplane 1/1 Running 0 9m52s
kube-system kube-flannel-ds-ghng8 1/1 Running 0 9m43s
kube-system kube-proxy-bpz6t 1/1 Running 0 9m43s
kube-system kube-scheduler-controlplane 1/1 Running 0 9m52s
root@controlplane:~#
root@controlplane:~# kubectl get deploy -n app-space
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
default-backend 1/1 1 1 3m41s
webapp-video 1/1 1 1 3m41s
webapp-wear 1/1 1 1 3m41s
root@controlplane:~#
root@controlplane:~# kubectl get ingress --all-namespaces
NAMESPACE NAME CLASS HOSTS ADDRESS PORTS AGE
app-space ingress-wear-watch <none> * 80 4m13s
root@controlplane:~#
root@controlplane:~# kubectl describe ingress ingress-wear-watch -n app-space
Name: ingress-wear-watch
Namespace: app-space
Address:
Default backend: default-http-backend:80 (<error: endpoints "default-http-backend" not found>)
Rules:
Host Path Backends
---- ---- --------
*
/wear wear-service:8080 (10.244.0.5:8080)
/watch video-service:8080 (10.244.0.6:8080)
Annotations: nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/rewrite-target: /
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/ssl-redirect: false
Events: <none>
root@controlplane:~#
root@controlplane:~# kubectl get svc -n app-space
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
default-http-backend ClusterIP 10.103.118.81 <none> 80/TCP 7m40s
video-service ClusterIP 10.102.90.47 <none> 8080/TCP 7m40s
wear-service ClusterIP 10.97.148.142 <none> 8080/TCP 7m40s
root@controlplane:~#
root@controlplane:~# kubectl get deploy -n app-space
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
default-backend 1/1 1 1 12m
webapp-food 1/1 1 1 27s
webapp-video 1/1 1 1 12m
webapp-wear 1/1 1 1 12m
root@controlplane:~#
root@controlplane:~# kubectl get svc -n app-space
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
default-http-backend ClusterIP 10.103.118.81 <none> 80/TCP 13m
food-service ClusterIP 10.98.163.89 <none> 8080/TCP 76s
video-service ClusterIP 10.102.90.47 <none> 8080/TCP 13m
wear-service ClusterIP 10.97.148.142 <none> 8080/TCP 13m
root@controlplane:~#
root@controlplane:~# kubectl get ingress -n app-space
NAME CLASS HOSTS ADDRESS PORTS AGE
ingress-wear-watch <none> * 80 13m
root@controlplane:~#
root@controlplane:~# kubectl get ingress -n app-space -o yaml
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
annotations:
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/rewrite-target: /
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/ssl-redirect: "false"
name: ingress-wear-watch
namespace: app-space
resourceVersion: "2024"
spec:
rules:
- http:
paths:
- backend:
service:
name: wear-service
port:
number: 8080
path: /wear
pathType: Prefix
- backend:
service:
name: video-service
port:
number: 8080
path: /stream
pathType: Prefix
root@controlplane:~#
root@controlplane:~# kubectl get namespaces
NAME STATUS AGE
app-space Active 20m
critical-space Active 37s
default Active 27m
ingress-space Active 20m
kube-node-lease Active 27m
kube-public Active 27m
kube-system Active 27m
root@controlplane:~# kubectl get all -n critical-space
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/webapp-pay-f74b9fc6-vpr59 1/1 Running 0 53s
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/pay-service ClusterIP 10.111.149.156 <none> 8282/TCP 53s
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
deployment.apps/webapp-pay 1/1 1 1 53s
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE
replicaset.apps/webapp-pay-f74b9fc6 1 1 1 53s
root@controlplane:~#
root@controlplane:~# vim pay-ingress.yaml
root@controlplane:~#
root@controlplane:~# kubectl apply -f pay-ingress.yaml -n critical-space
ingress.networking.k8s.io/test-ingress created
root@controlplane:~#
ingress_rule
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
annotations:
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/rewrite-target: /
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/ssl-redirect: "false"
name: ingress-wear-watch
namespace: app-space
resourceVersion: "2024"
spec:
rules:
- http:
paths:
- backend:
service:
name: wear-service
port:
number: 8080
path: /wear
pathType: Prefix
- backend:
service:
name: video-service
port:
number: 8080
path: /stream
pathType: Prefix
ingress_rule2
---
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: test-ingress
namespace: critical-space
annotations:
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/rewrite-target: /
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/ssl-redirect: "false"
spec:
rules:
- http:
paths:
- path: /pay
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: pay-service
port:
number: 8282
nginxingress_ncontrollerlabs
root@controlplane:~# kubectl get all --all-namespaces
NAMESPACE NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
app-space pod/default-backend-5cf9bfb9d-xkrb8 1/1 Running 0 2m25s
app-space pod/webapp-video-84f8655bd8-htjjm 1/1 Running 0 2m25s
app-space pod/webapp-wear-6ff9445955-d2pn6 1/1 Running 0 2m24s
kube-system pod/coredns-74ff55c5b-vcptv 1/1 Running 0 4m19s
kube-system pod/coredns-74ff55c5b-zspgq 1/1 Running 0 4m19s
kube-system pod/etcd-controlplane 1/1 Running 0 4m30s
kube-system pod/kube-apiserver-controlplane 1/1 Running 0 4m30s
kube-system pod/kube-controller-manager-controlplane 1/1 Running 0 4m30s
kube-system pod/kube-flannel-ds-ss84c 1/1 Running 0 4m20s
kube-system pod/kube-proxy-89b88 1/1 Running 0 4m20s
kube-system pod/kube-scheduler-controlplane 1/1 Running 0 4m30s
NAMESPACE NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
app-space service/default-http-backend ClusterIP 10.106.141.152 <none> 80/TCP 2m24s
app-space service/video-service ClusterIP 10.103.191.8 <none> 8080/TCP 2m25s
app-space service/wear-service ClusterIP 10.107.70.55 <none> 8080/TCP 2m25s
default service/kubernetes ClusterIP 10.96.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 4m39s
kube-system service/kube-dns ClusterIP 10.96.0.10 <none> 53/UDP,53/TCP,9153/TCP 4m37s
NAMESPACE NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE NODE SELECTOR AGE
kube-system daemonset.apps/kube-flannel-ds 1 1 1 1 1 <none> 4m34s
kube-system daemonset.apps/kube-proxy 1 1 1 1 1 kubernetes.io/os=linux 4m37s
NAMESPACE NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
app-space deployment.apps/default-backend 1/1 1 1 2m25s
app-space deployment.apps/webapp-video 1/1 1 1 2m25s
app-space deployment.apps/webapp-wear 1/1 1 1 2m25s
kube-system deployment.apps/coredns 2/2 2 2 4m37s
NAMESPACE NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE
app-space replicaset.apps/default-backend-5cf9bfb9d 1 1 1 2m25s
app-space replicaset.apps/webapp-video-84f8655bd8 1 1 1 2m25s
app-space replicaset.apps/webapp-wear-6ff9445955 1 1 1 2m25s
kube-system replicaset.apps/coredns-74ff55c5b 2 2 2 4m20s
root@controlplane:~#
root@controlplane:~# kubectl create namespace ingress-space
namespace/ingress-space created
root@controlplane:~#
root@controlplane:~# kubectl get namespaces
NAME STATUS AGE
app-space Active 7m45s
default Active 9m59s
ingress-space Active 30s
kube-node-lease Active 10m
kube-public Active 10m
kube-system Active 10m
root@controlplane:~#
The NGINX Ingress Controller requires a ConfigMap object. Create a ConfigMap object in the ingress-space.
root@controlplane:~#kubectl create configmap nginx-configuration --namespace ingress-space
root@controlplane:~# kubectl get cm -n ingress-space
NAME DATA AGE
kube-root-ca.crt 1 3m5s
nginx-configuration 0 27s
root@controlplane:~#
root@controlplane:~# kubectl create sa ingress-serviceaccount -n ingress-space
serviceaccount/ingress-serviceaccount created
root@controlplane:~#
root@controlplane:~# kubectl get sa -n ingress-space
NAME SECRETS AGE
default 1 4m47s
ingress-serviceaccount 1 21s
root@controlplane:~#
Create Role and Rolebindings for the service account
root@controlplane:~# kubectl get roles -n ingress-space -o wide
NAME CREATED AT
ingress-role 2021-09-28T06:01:47Z
root@controlplane:~# kubectl get rolebindings -n ingress-space -o wide
NAME ROLE AGE USERS GROUPS SERVICEACCOUNTS
ingress-role-binding Role/ingress-role 83s /ingress-serviceaccount
root@controlplane:~#
root@controlplane:~# kubectl describe role ingress-role -n ingress-space
Name: ingress-role
Labels: app.kubernetes.io/name=ingress-nginx
app.kubernetes.io/part-of=ingress-nginx
Annotations: <none>
PolicyRule:
Resources Non-Resource URLs Resource Names Verbs
--------- ----------------- -------------- -----
configmaps [] [] [get create]
configmaps [] [ingress-controller-leader-nginx] [get update]
endpoints [] [] [get]
namespaces [] [] [get]
pods [] [] [get]
secrets [] [] [get]
root@controlplane:~#
root@controlplane:~# kubectl describe rolebindings ingress-role-binding -n ingress-space
Name: ingress-role-binding
Labels: app.kubernetes.io/name=ingress-nginx
app.kubernetes.io/part-of=ingress-nginx
Annotations: <none>
Role:
Kind: Role
Name: ingress-role
Subjects:
Kind Name Namespace
---- ---- ---------
ServiceAccount ingress-serviceaccount
root@controlplane:~#
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: ingress-controller
namespace: ingress-space
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
name: nginx-ingress
template:
metadata:
labels:
name: nginx-ingress
spec:
serviceAccountName: ingress-serviceaccount
containers:
- name: nginx-ingress-controller
image: quay.io/kubernetes-ingress-controller/nginx-ingress-controller:0.21.0
args:
- /nginx-ingress-controller
- --configmap=$(POD_NAMESPACE)/nginx-configuration
- --default-backend-service=app-space/default-http-backend
env:
- name: POD_NAME
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.name
- name: POD_NAMESPACE
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.namespace
ports:
- name: http
containerPort: 80
- name: https
containerPort: 443
root@controlplane:~# kubectl get all -n ingress-space
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/ingress-controller-5857685bf-d9kkm 1/1 Running 0 5m54s
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
deployment.apps/ingress-controller 1/1 1 1 5m54s
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE
replicaset.apps/ingress-controller-5857685bf 1 1 1 5m54s
root@controlplane:~#
create a service to make Ingress available to external users.
Name: ingress
Type: NodePort
Port: 80
TargetPort: 80
NodePort: 30080
Namespace: ingress-space
Use the right selector
root@controlplane:~# kubectl expose deployment ingress-controller --type=NodePort --port=80 --name=ingress -n ingress-space --dry-run=client -o yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
creationTimestamp: null
name: ingress
spec:
ports:
- port: 80
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 80
selector:
name: nginx-ingress
type: NodePort
status:
loadBalancer: {}
root@controlplane:~#
root@controlplane:~# kubectl apply -f ingress_controller_service.yaml -n ingress-space
service/ingress created
root@controlplane:~# kubectl get all -n ingress-space
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/ingress-controller-5857685bf-d9kkm 1/1 Running 0 18m
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/ingress NodePort 10.101.203.157 <none> 80:30080/TCP,443:30404/TCP 17s
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
deployment.apps/ingress-controller 1/1 1 1 18m
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE
replicaset.apps/ingress-controller-5857685bf 1 1 1 18m
root@controlplane:~#
root@controlplane:~# kubectl get all -n app-space
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/default-backend-5cf9bfb9d-xkrb8 1/1 Running 0 37m
pod/webapp-video-84f8655bd8-htjjm 1/1 Running 0 37m
pod/webapp-wear-6ff9445955-d2pn6 1/1 Running 0 37m
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/default-http-backend ClusterIP 10.106.141.152 <none> 80/TCP 37m
service/video-service ClusterIP 10.103.191.8 <none> 8080/TCP 37m
service/wear-service ClusterIP 10.107.70.55 <none> 8080/TCP 37m
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
deployment.apps/default-backend 1/1 1 1 37m
deployment.apps/webapp-video 1/1 1 1 37m
deployment.apps/webapp-wear 1/1 1 1 37m
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE
replicaset.apps/default-backend-5cf9bfb9d 1 1 1 37m
replicaset.apps/webapp-video-84f8655bd8 1 1 1 37m
replicaset.apps/webapp-wear-6ff9445955 1 1 1 37m
root@controlplane:~#
Create the ingress resource to make the applications available at /wear and /watch on the Ingress service.
Create the ingress in the app-space
#----------------------------------------------------------------------------
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: ingress-wear-watch
namespace: app-space
annotations:
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/rewrite-target: /
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/ssl-redirect: "false"
spec:
rules:
- http:
paths:
- path: /wear
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: wear-service
port:
number: 8080
- path: /watch
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: video-service
port:
number: 8080
#-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
root@controlplane:~# kubectl apply -f ingress-resource-rule.yaml -n app-space
ingress.networking.k8s.io/ingress-wear-watch created
root@controlplane:~#
root@controlplane:~# kubectl get ingress -n app-space
NAME CLASS HOSTS ADDRESS PORTS AGE
ingress-wear-watch <none> * 80 36s
root@controlplane:~# kubectl describe ingress ingress-wear-watch -n app-space
Name: ingress-wear-watch
Namespace: app-space
Address:
Default backend: default-http-backend:80 (<error: endpoints "default-http-backend" not found>)
Rules:
Host Path Backends
---- ---- --------
*
/wear wear-service:8080 (10.244.0.5:8080)
/watch video-service:8080 (10.244.0.4:8080)
Annotations: nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/rewrite-target: /
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/ssl-redirect: false
Events: <none>
root@controlplane:~#
nginx_ingress_deploy
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: ingress-controller
namespace: ingress-space
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
name: nginx-ingress
template:
metadata:
labels:
name: nginx-ingress
spec:
serviceAccountName: ingress-serviceaccount
containers:
- name: nginx-ingress-controller
image: quay.io/kubernetes-ingress-controller/nginx-ingress-controller:0.21.0
args:
- /nginx-ingress-controller
- --configmap=$(POD_NAMESPACE)/nginx-configuration
- --default-backend-service=app-space/default-http-backend
env:
- name: POD_NAME
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.name
- name: POD_NAMESPACE
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.namespace
ports:
- name: http
containerPort: 80
- name: https
containerPort: 443
nginx_ingress_service
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: ingress
namespace: ingress-space
spec:
type: NodePort
ports:
- port: 80
targetPort: 80
protocol: TCP
nodePort: 30080
name: http
- port: 443
targetPort: 443
protocol: TCP
name: https
selector:
name: nginx-ingress
configure_ingress_rule
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: ingress-wear-watch
namespace: app-space
annotations:
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/rewrite-target: /
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/ssl-redirect: "false"
spec:
rules:
- http:
paths:
- path: /wear
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: wear-service
port:
number: 8080
- path: /watch
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: video-service
port:
number: 8080